































Engine Systems

Drivetrain Systems

Suspension & Steering

Brake Systems

Dust cover Series

Air Conditioning System

Filter Series

Exhaust Gas Systems

Fastening Series

Body parts

Electrical Parts

Automotive lighting

Tire Repair Supplies

Chemical Goods Series

Lubricants & Fluids Series

Service tools & Equipment

Others



















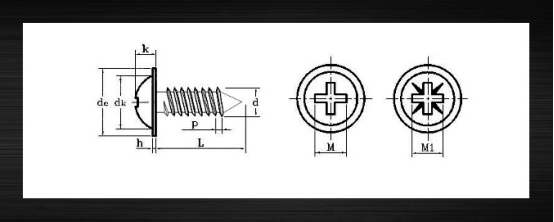
Self Tapping Screw Bolt
Among the many ways of joining automotive parts, screwing is a more common way of fixing and joining than welding, gluing and snap connections.
Tapping screws are used in the connection of metallic or non-metallic materials without pre-drilling of the threads. Important dimensions include the large and small diameter of the thread, the pitch and the angle of the thread.
For thermoplastic connections, the internal threads in the mounting holes are forcibly extruded by rotating tapping screws, whereas for parts made from harder thermoset plastics, the internal threads in the mounting holes can be cut by rotating tapping screws.
Tapping screws are made of high manganese low carbon penetration steel (1022A), heat hardened (carburised) and finished with black zinc to prevent rust. The stainless steel tapping screws are solution hardened to achieve the standard mechanical and service properties required for tapping screws, high surface hardness and good core toughness.
The main advantages of tapping screws for tightening connections are as follows.
1. easy to achieve automation;
2. high connection strength;
3. low probability of cracking under stress;
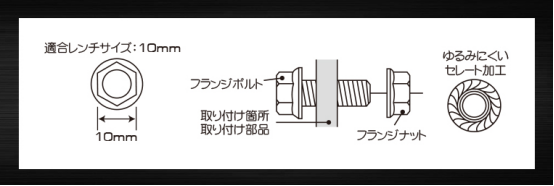
Bolts, the most used component in automobiles, are divided into two types according to the direction of winding of the threads: left-hand threads and right-hand threads. The vast majority of threads are right-hand threads, with a very small number of special parts using left-hand threads.
The number of threads can be divided into single threads, double threads and triple threads, with single threads being used for connections and others for transmission.
The thread shape is divided into triangular, rectangular, trapezoidal and serrated threads. The triangular thread has good self-locking properties and high thread strength, and is generally used for connections, making it the most widely used thread.
The coarse thread is the basic thread and the fine thread has high strength, but the strength of the threaded tooth is lower than that of the coarse thread and is generally used for thin-walled fittings, shaft parts and adjustment parts of precision mechanisms.
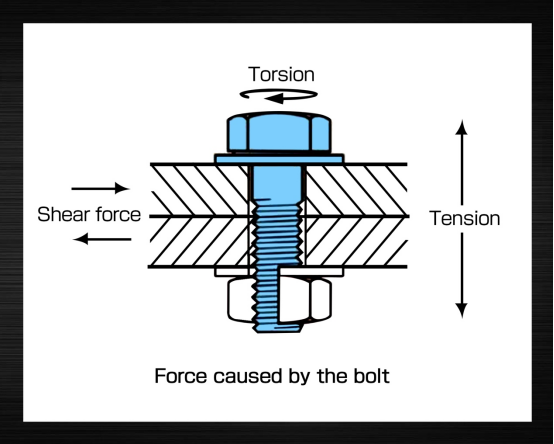
The purpose of the threaded fastener connection is to make the connected parts fit tightly and withstand certain external forces, with the advantages of high precision, easy assembly and easy disassembly of parts.
The greater the axial clamping force of the bolt, the better its resistance to loosening and fatigue performance, usually the best results when the bolt is tightened to yield.
Notes on the use of threaded fasteners:
1. Different thread types should not be used interchangeably, as this may result in damage to the threads.
2. Bolts and nuts are divided into right-hand and left-hand threads according to the direction in which they are screwed in, but left-hand threads are not commonly used and are stamped with the letter "L", while right-hand threads are more commonly used.
3. The use of a predetermined tightening torque is the most common method of controlling fastener tension. Axial tension is proportional to the torque applied under certain conditions, the most common of which are clean, dry, good threads.
4. Note that the torque for tightening threaded parts is for clean and oil-free conditions. Oiled threaded parts may have an unstable or insufficient clamping force on the component even after being tightened to the specified torque.
Among the many ways of joining automotive parts, screwing is a more common way of fixing and joining than welding, gluing and snap connections.