Quick Link
PATCH COLD
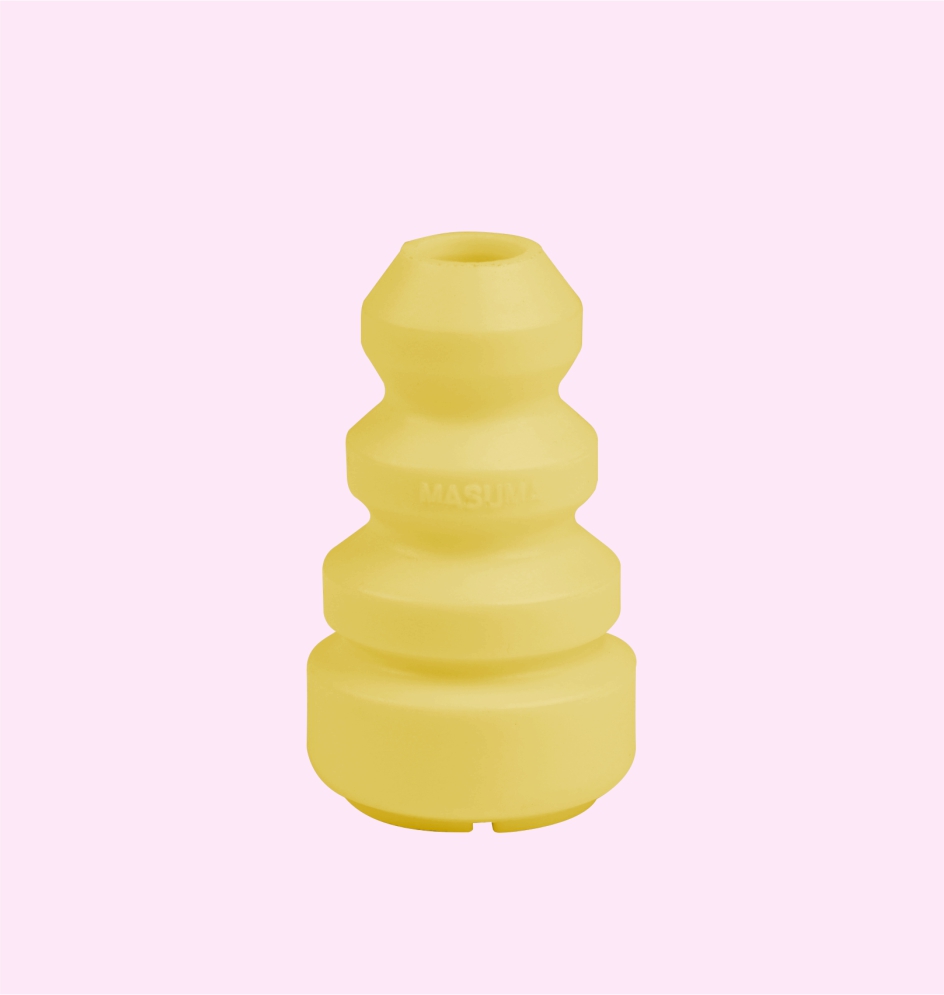
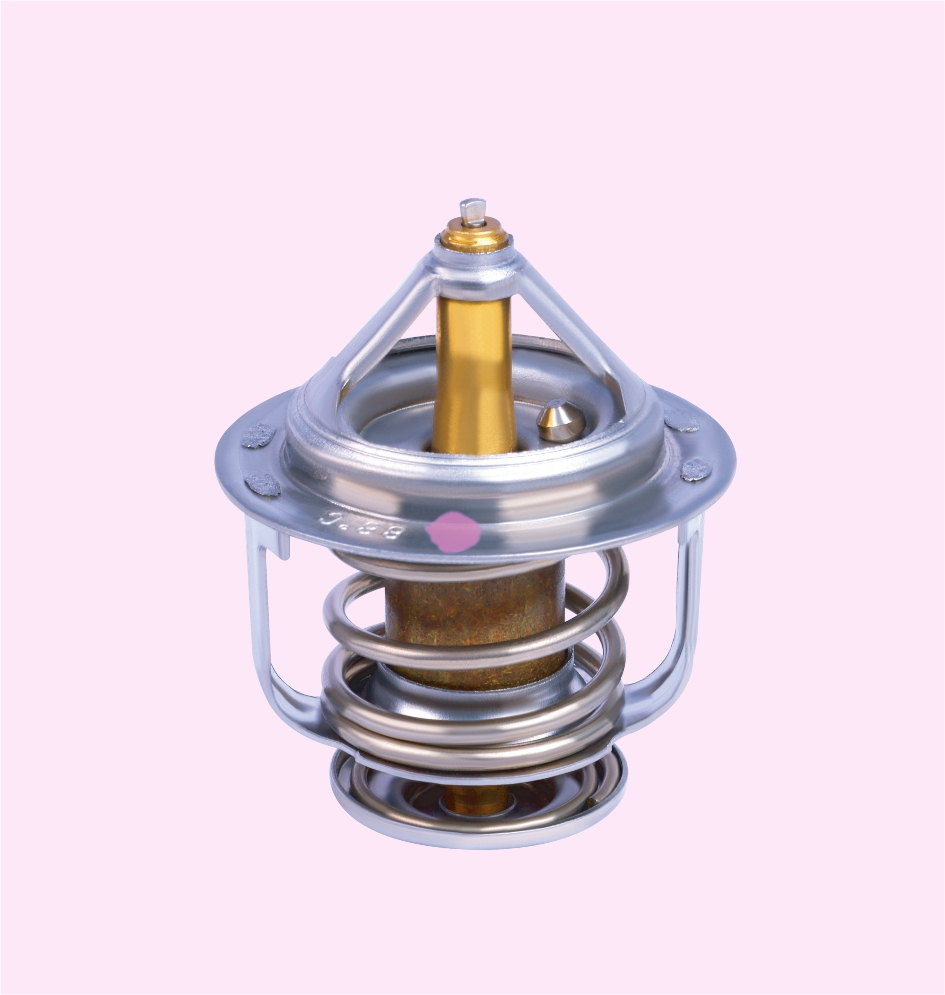
THERMOSTAT
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID
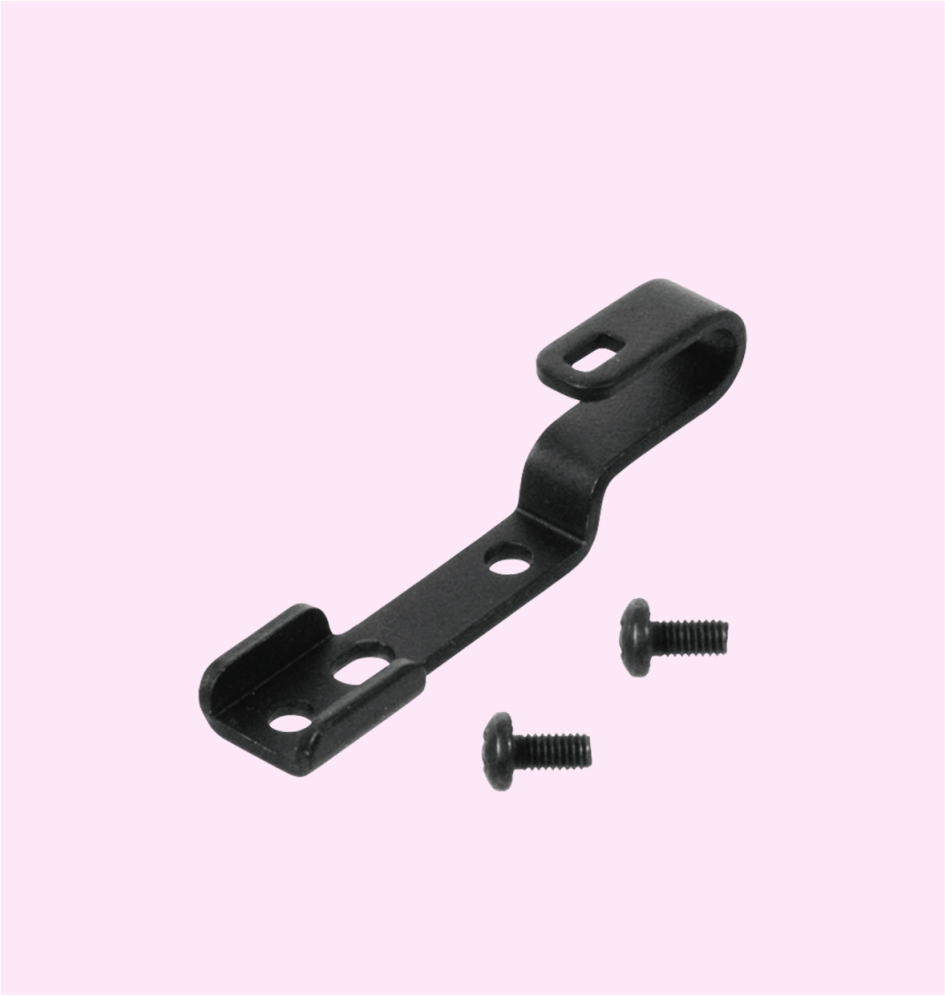
BATTERY RETAINING CLAMP
COOLANT
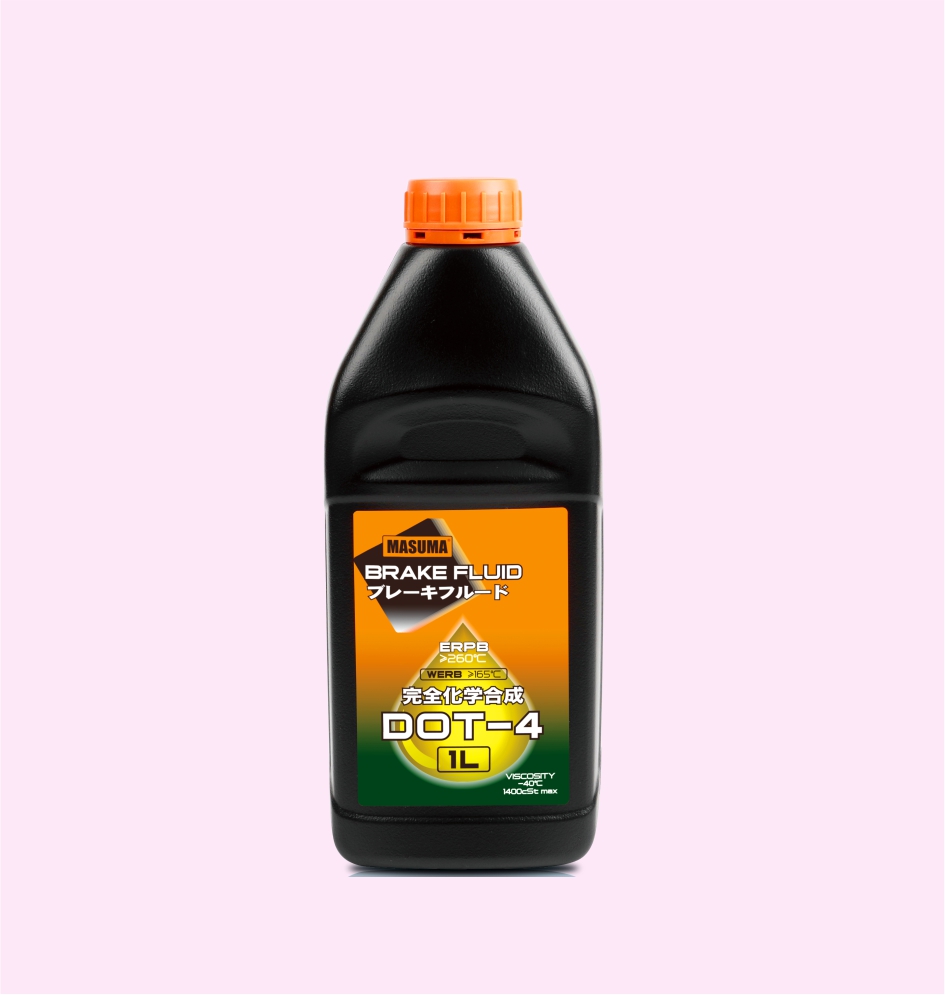
BRAKE FLUID
CLUTCH DISC
AUTOMOTIVE FUSE
REFRIGERANT
BATTERY INTAKE FILTER
OXYGEN SENSOR
IGNITION COILS
TIRE PLUG KIT
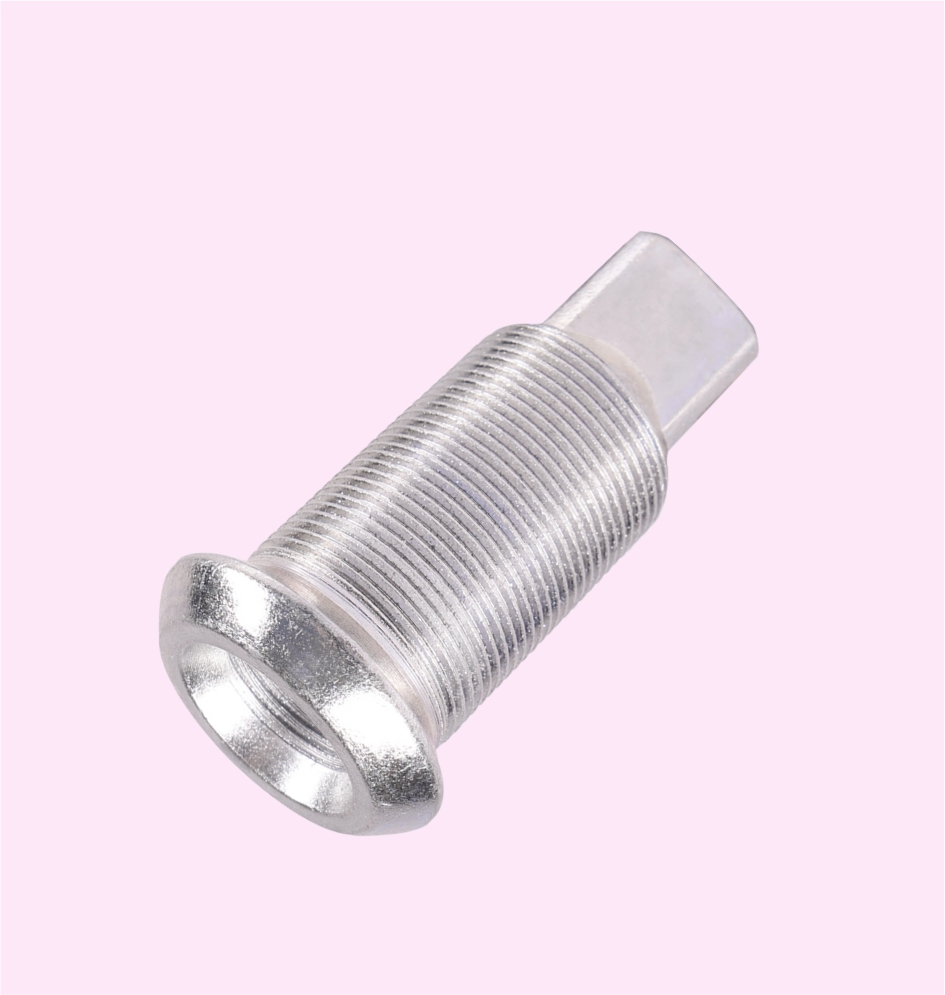
HUB BOLT
AIR FLOW SENSOR
RTV SILICONE
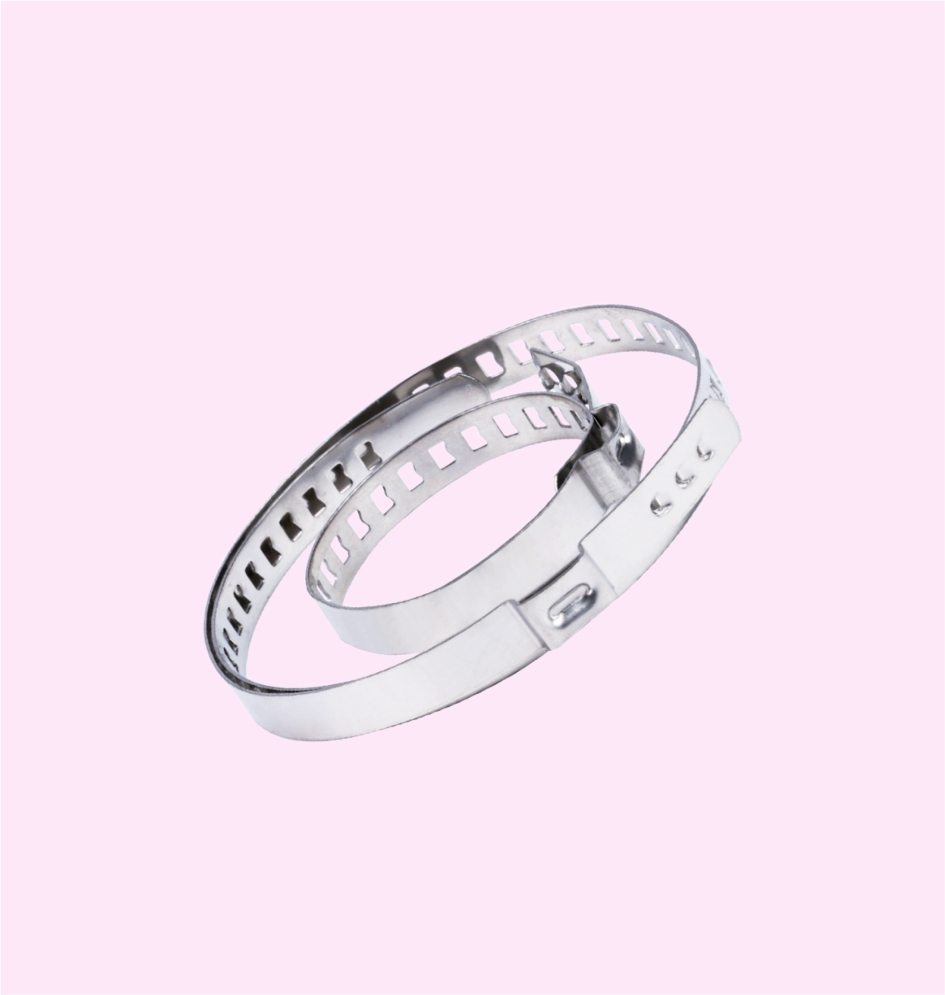
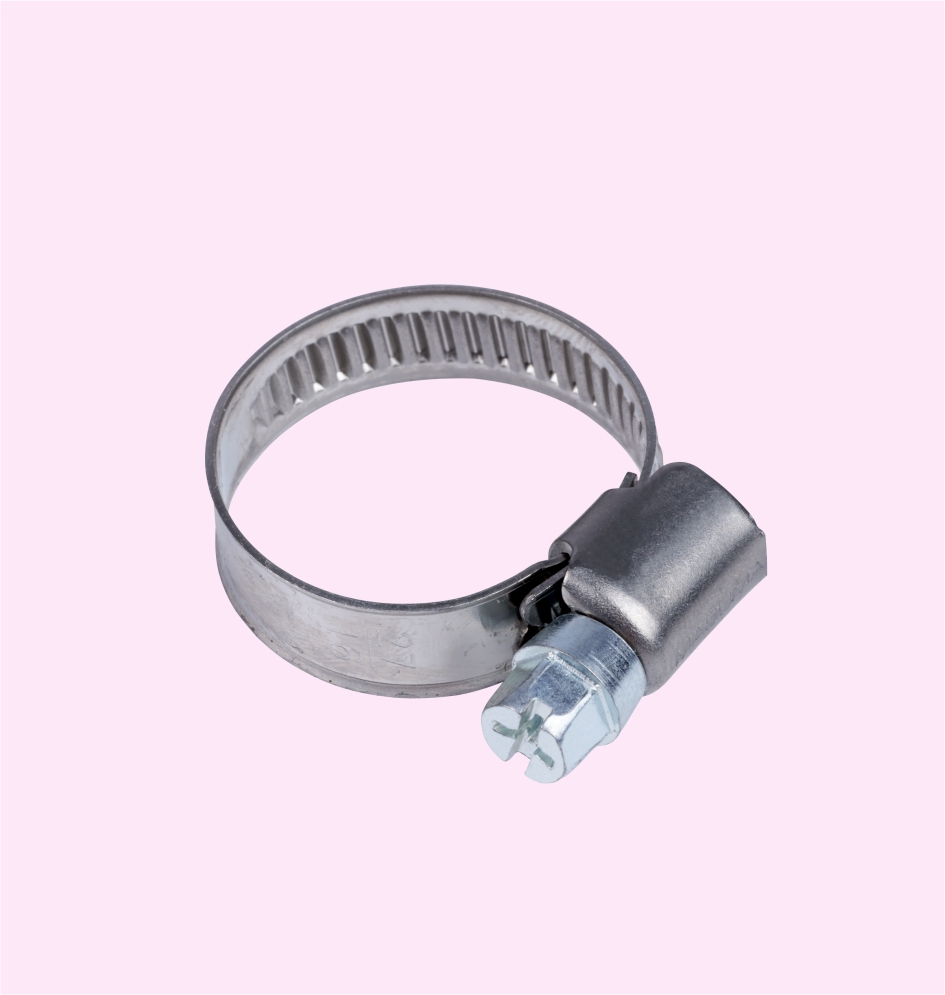
HOSE CLAMP
GREASE FITTING
STARTER CONTACTS
SPARK PLUGS
GLOW PLUG
VULCANIZING CEMENT
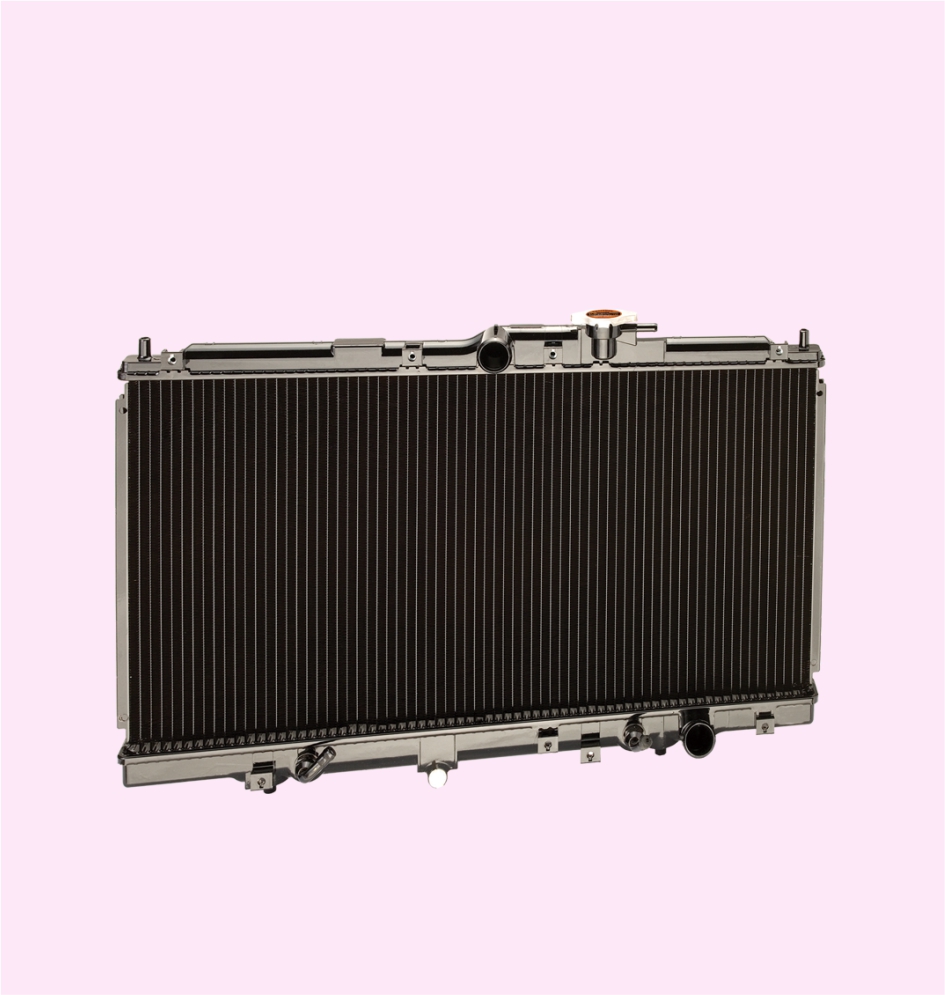
RADIATOR
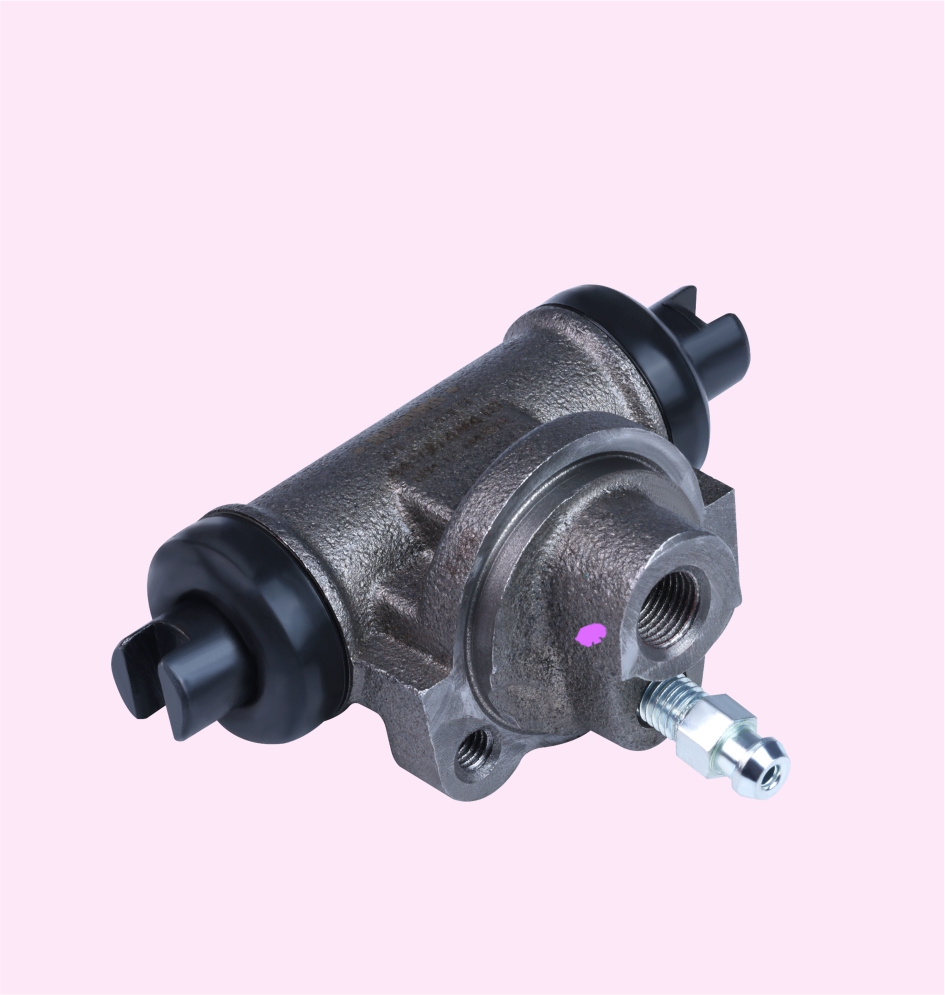
WHEEL CYLINDER
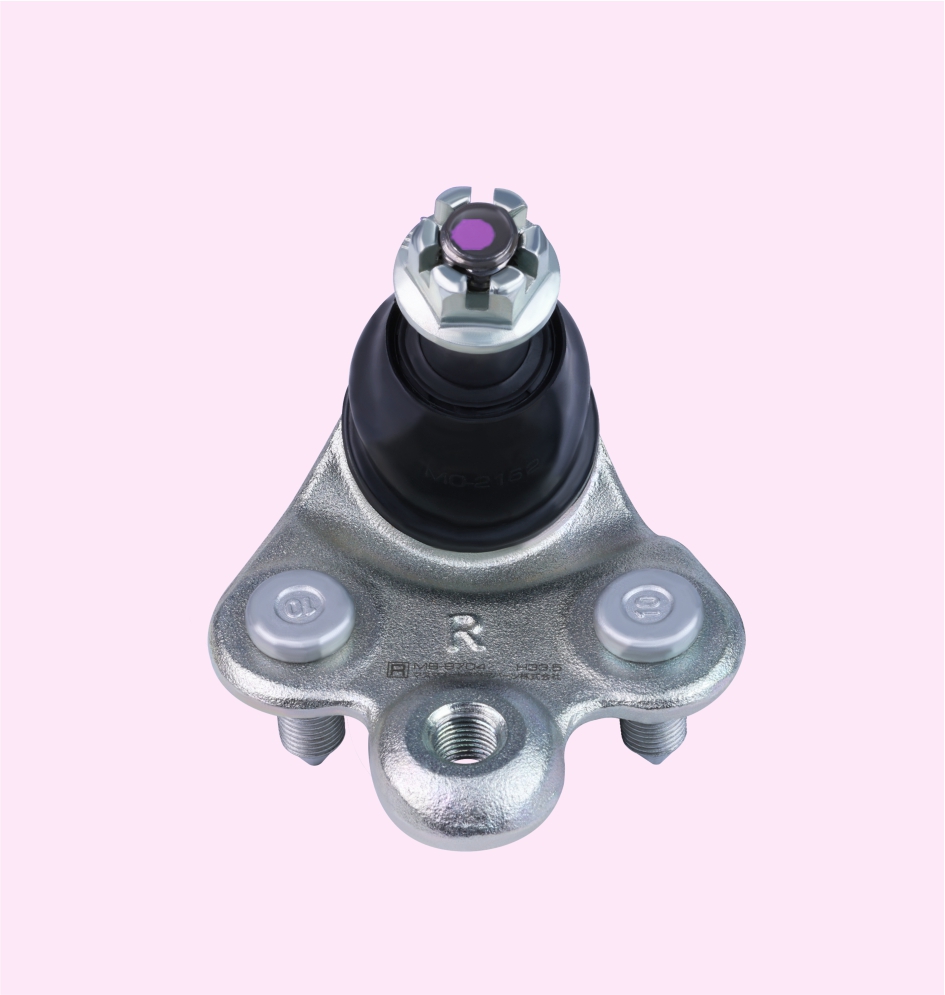
BALL JOINT
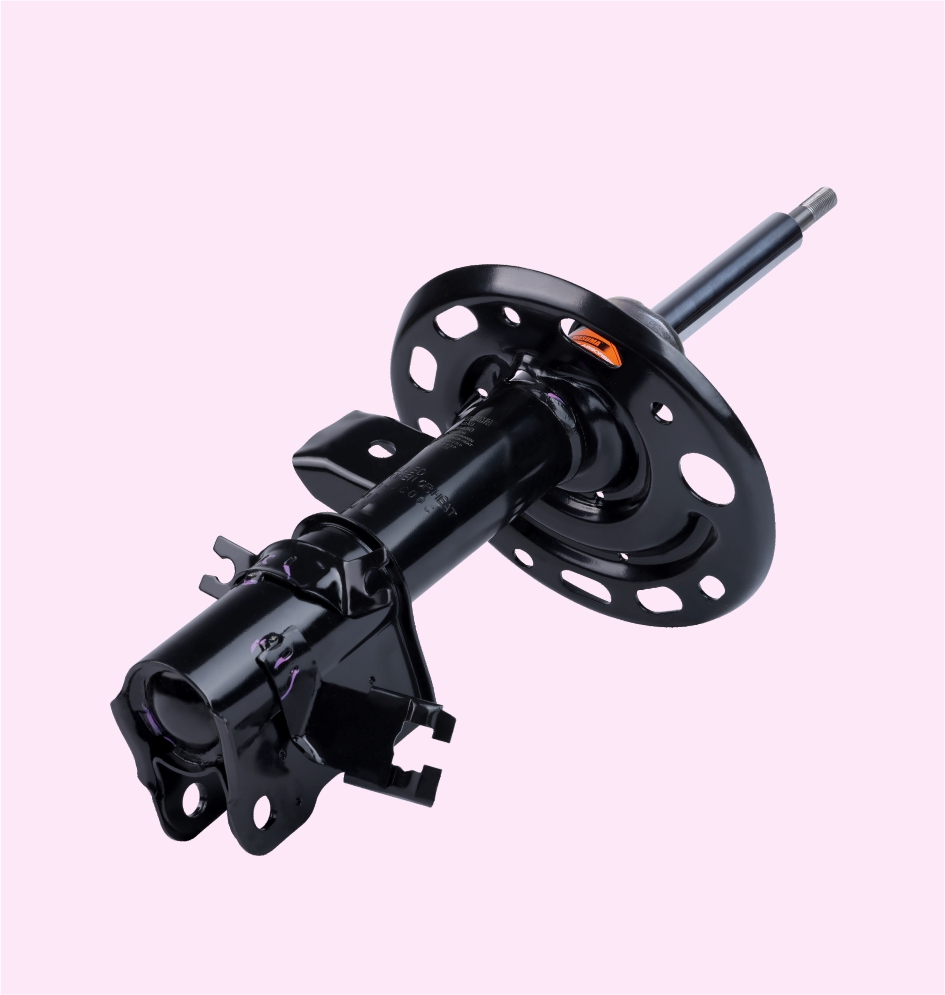
SHOCK ABSORBERS
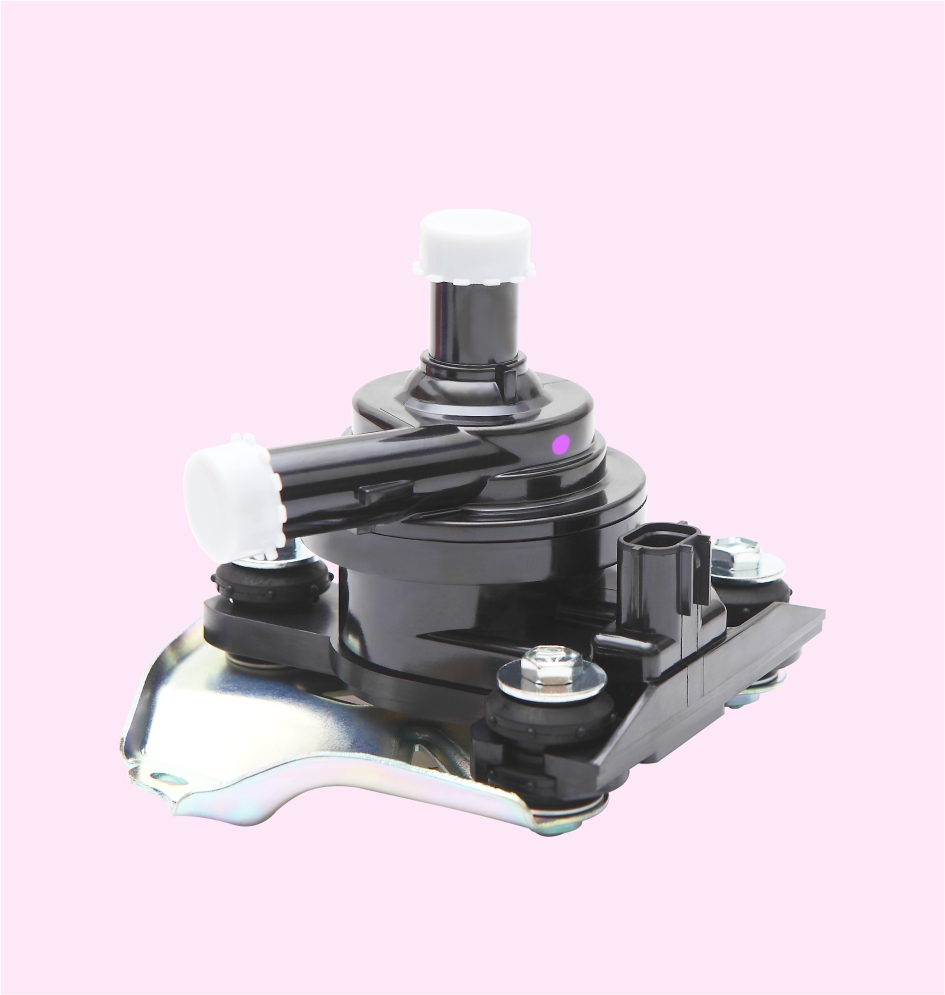
ENGINE MOUNTING
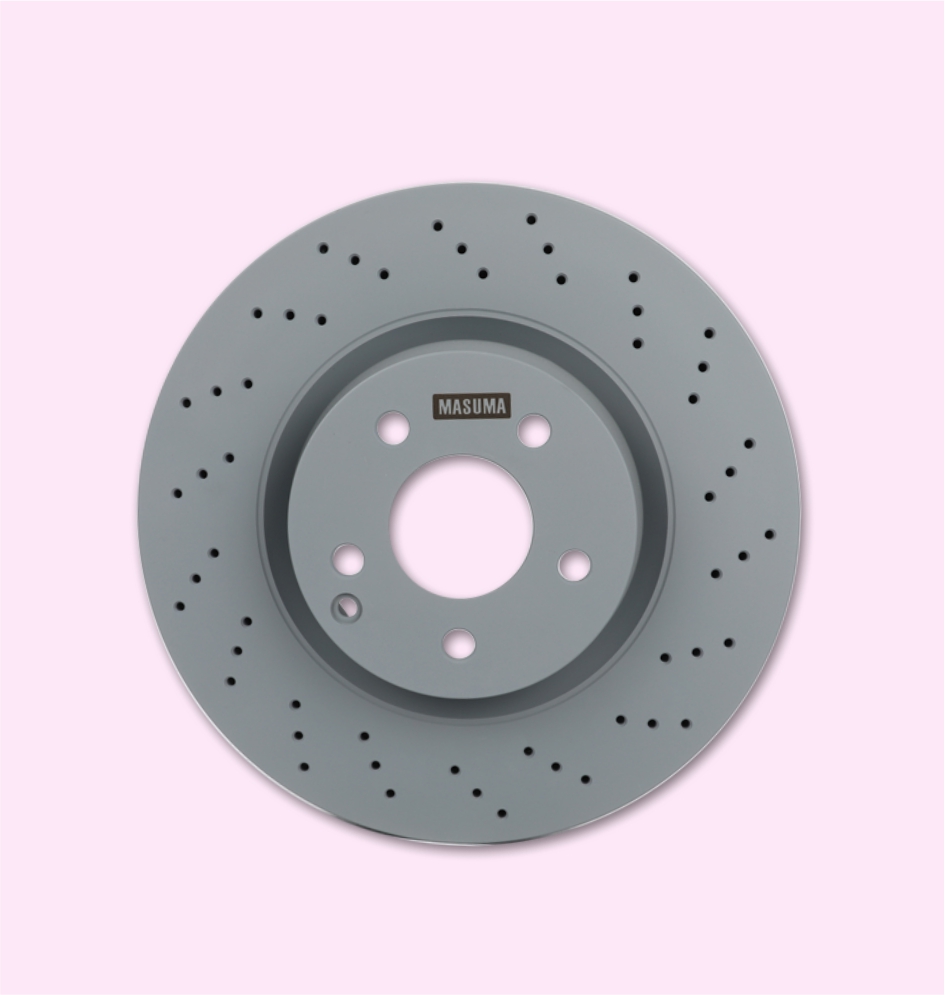
BRAKE DISC
BRAKE & PARTS CLEANER
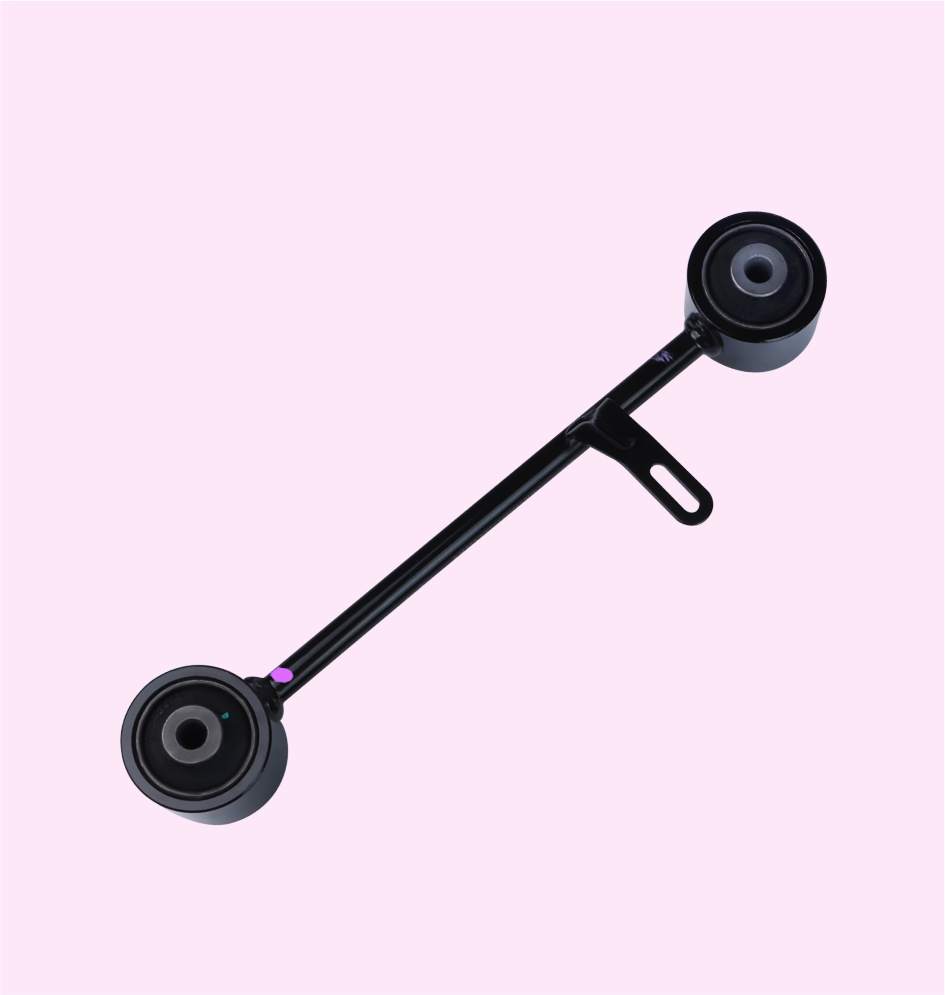
CONTROL ROD
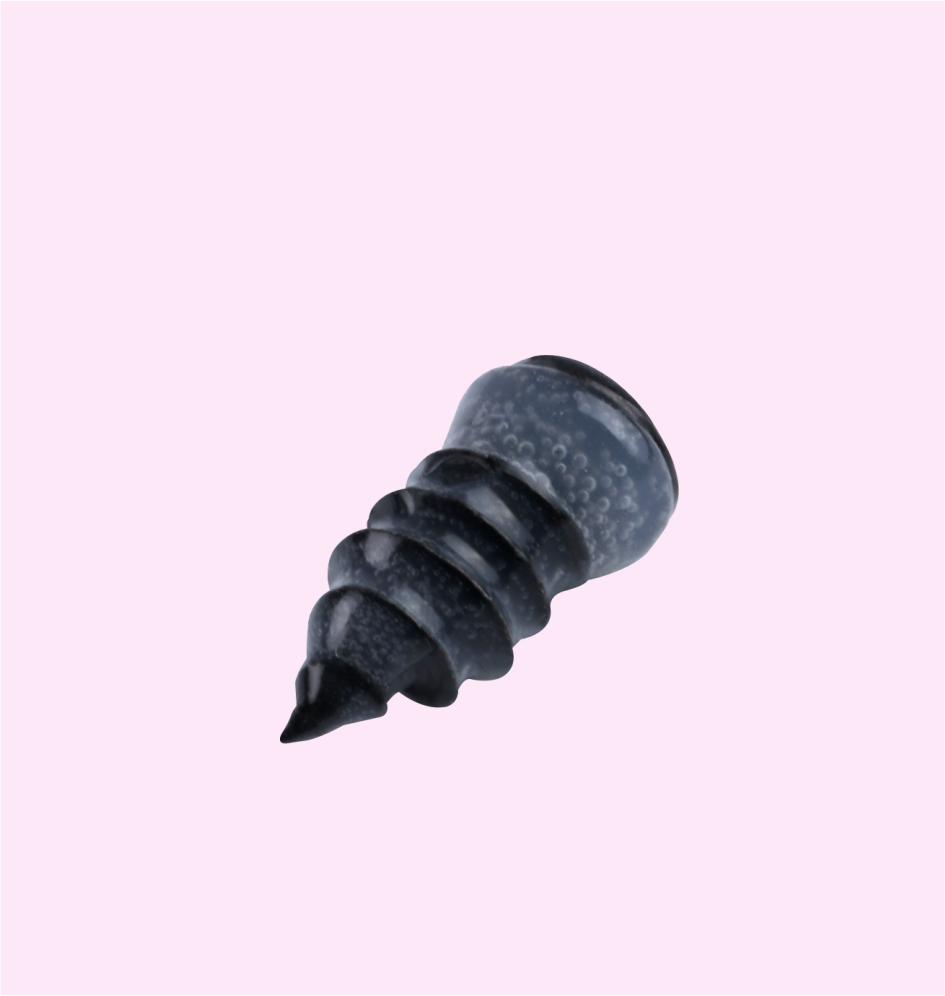
TAPPING SCREW
ENGINE GASKET
MOTOR OIL
FUEL PUMP STRAINER
SPARK PLUG CABLE SET
INJECTOR WASHERS
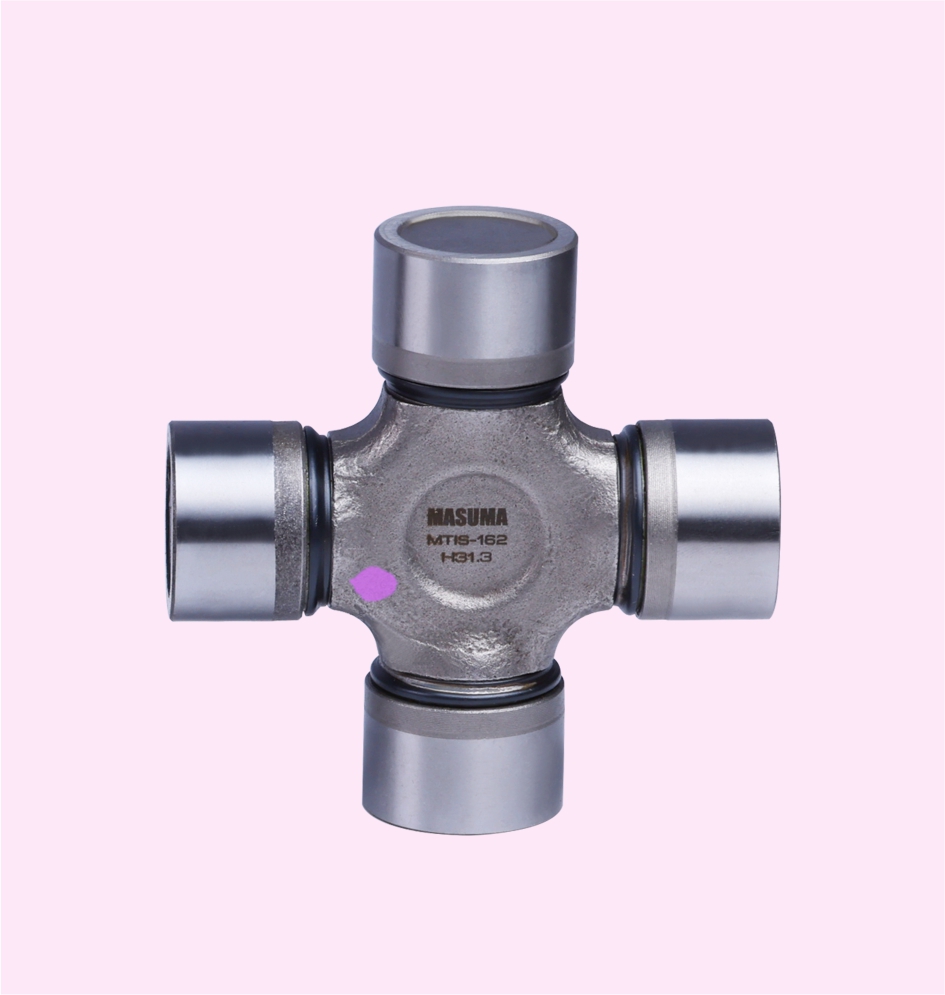
UNIVERSAL JOINT
WHEEL NUT
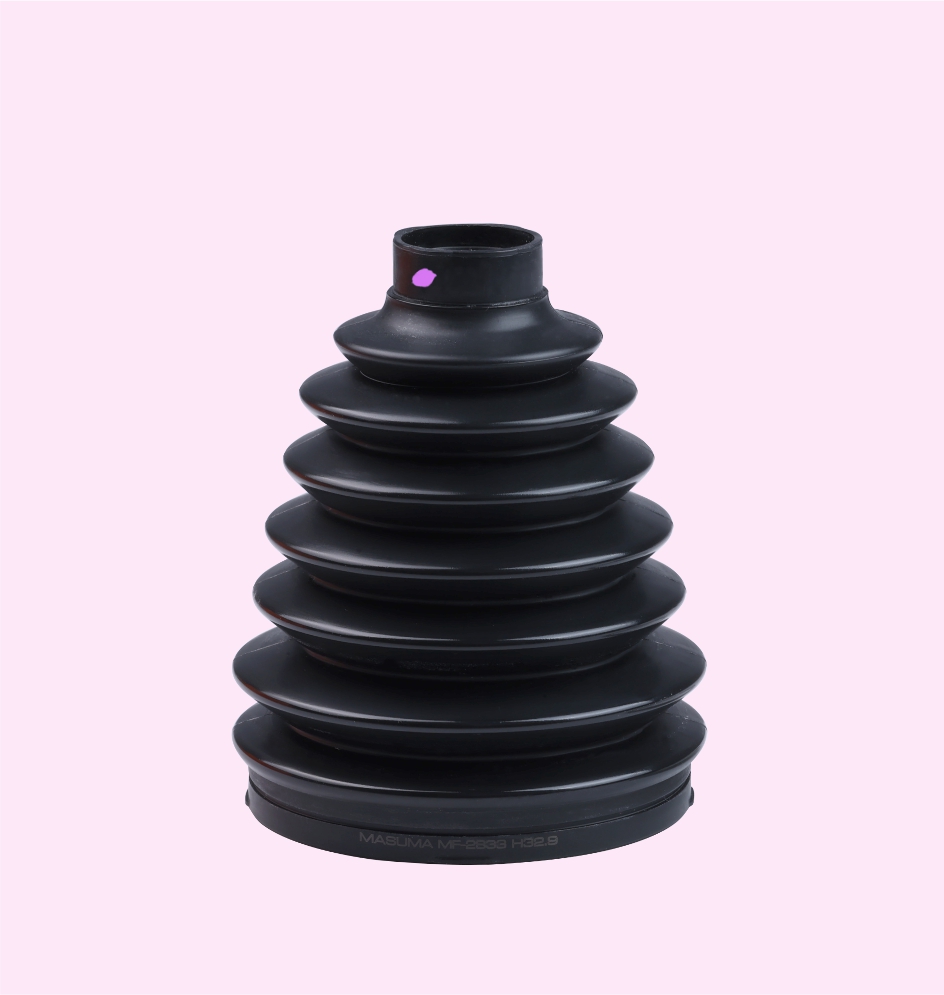
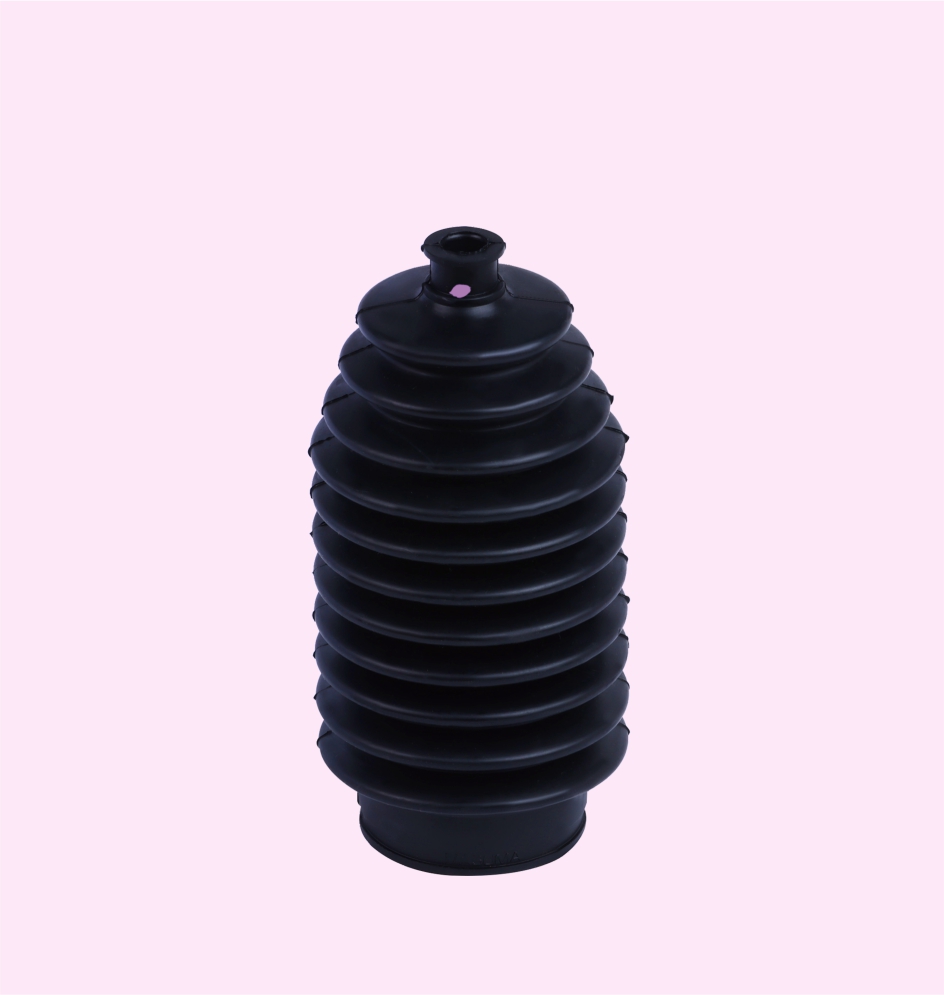
STEERING BOOT
OUTER C.V. JOINT
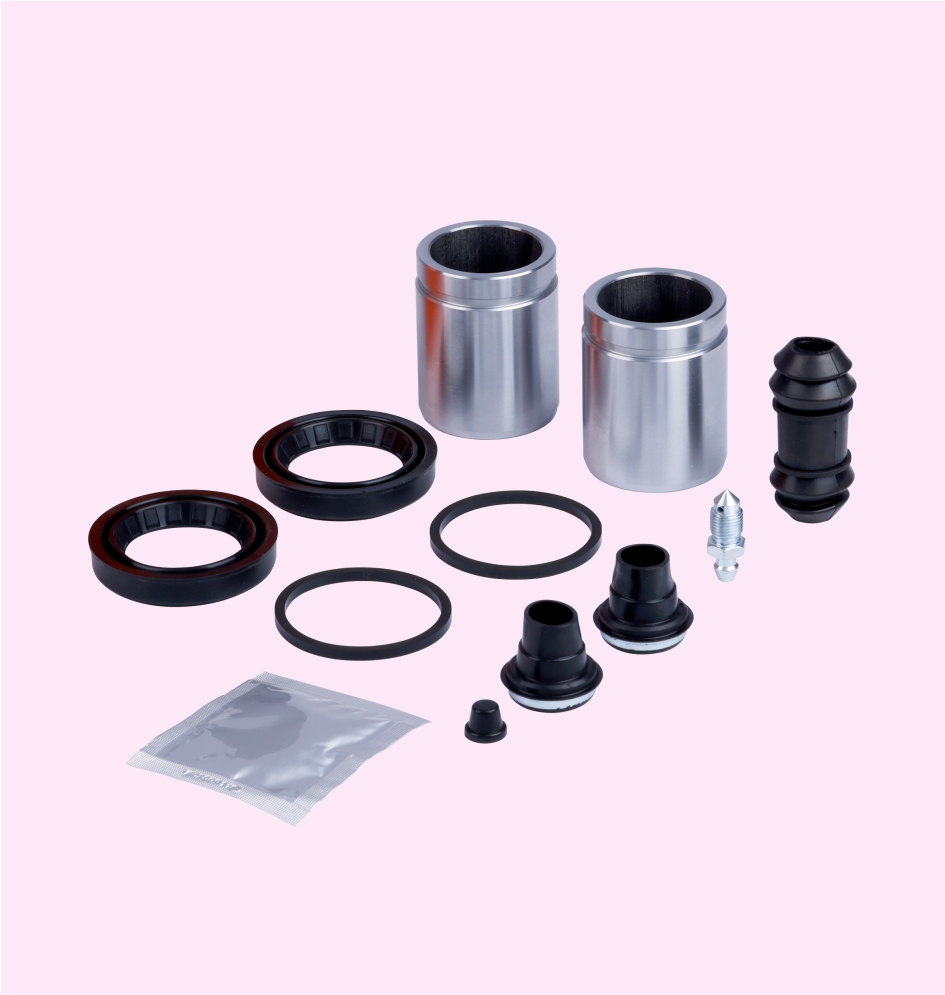
DISC BRAKE SEAL KIT
CABIN FILTER
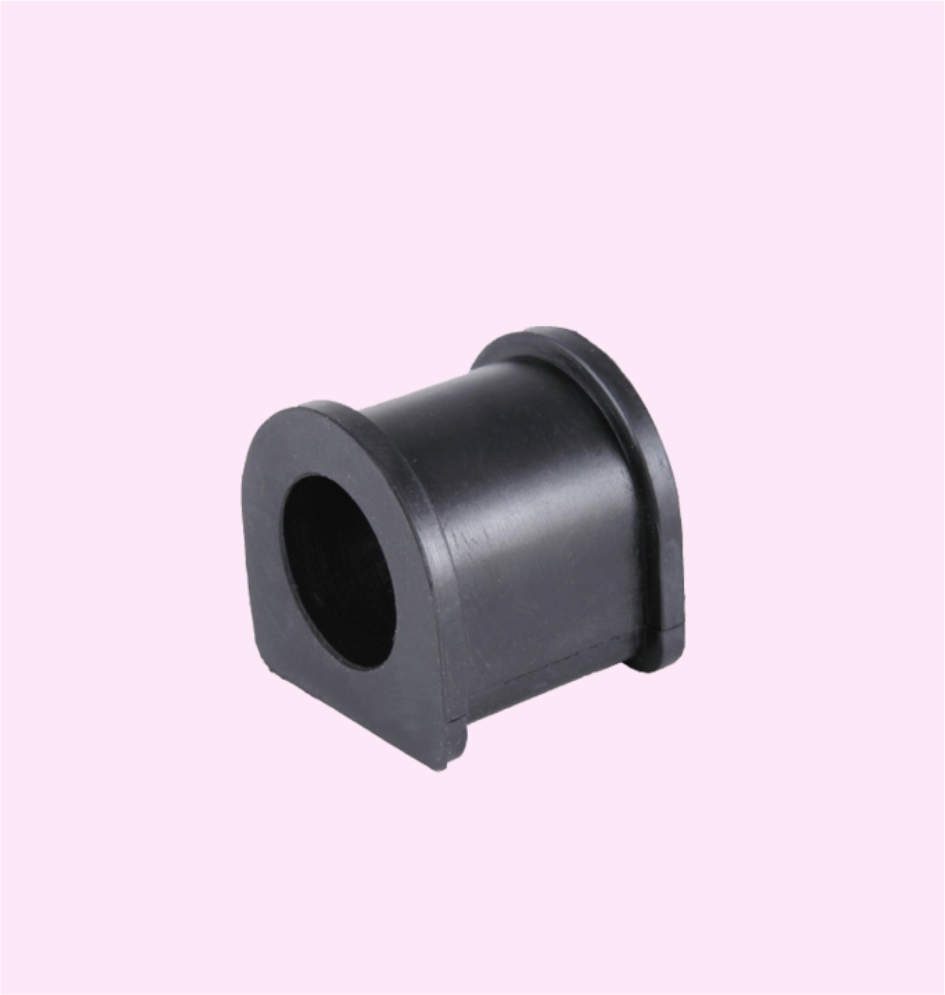
STABILIZER BUSH
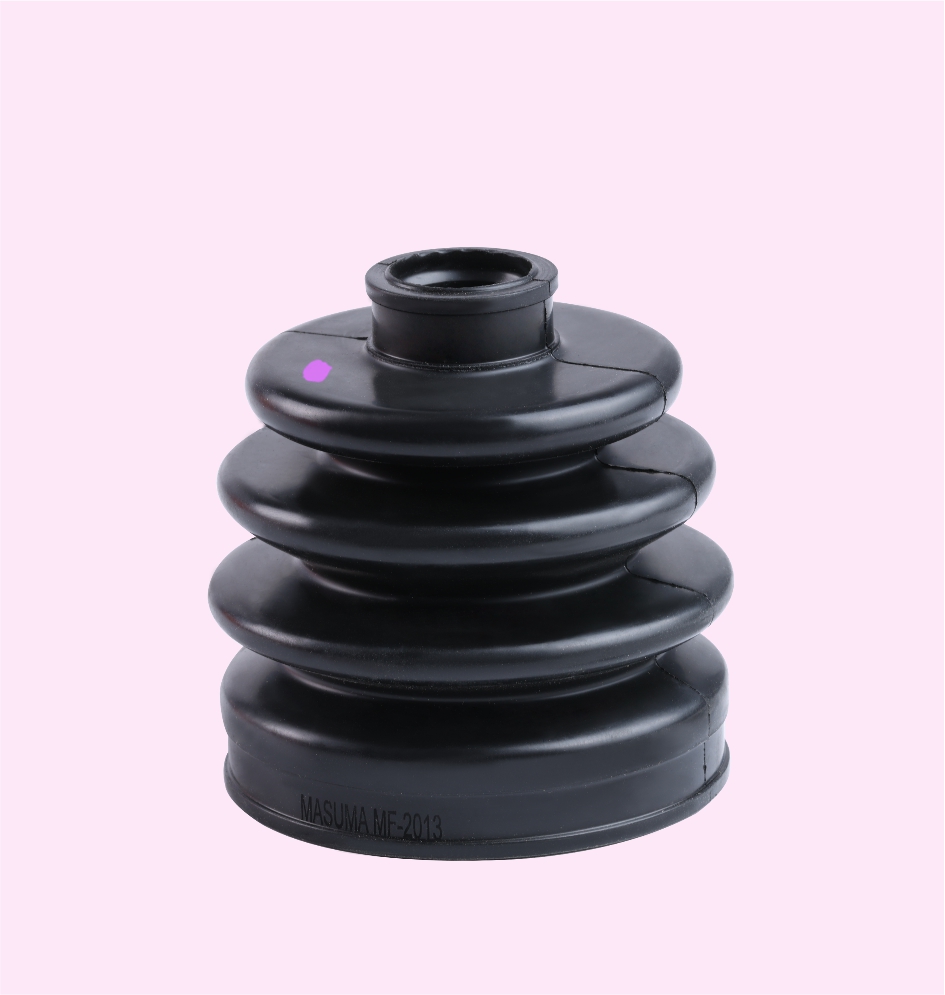
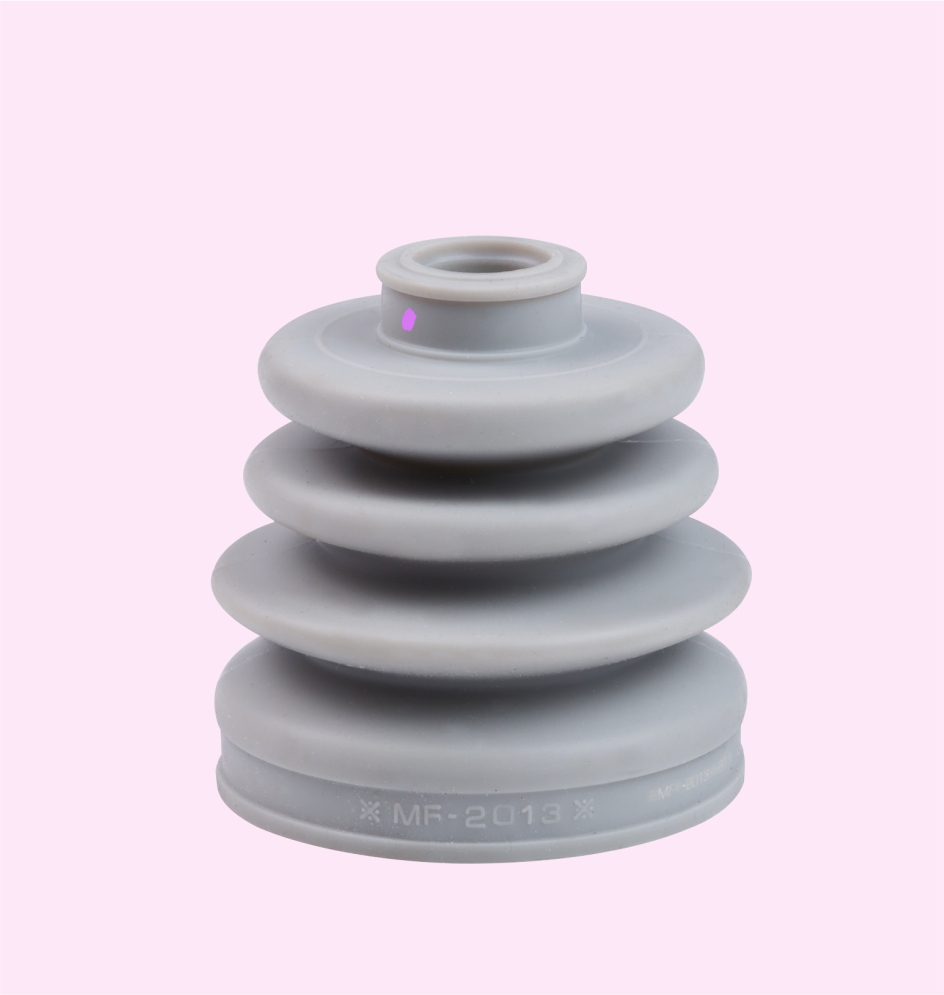
DRIVE SHAFT BOOT KIT
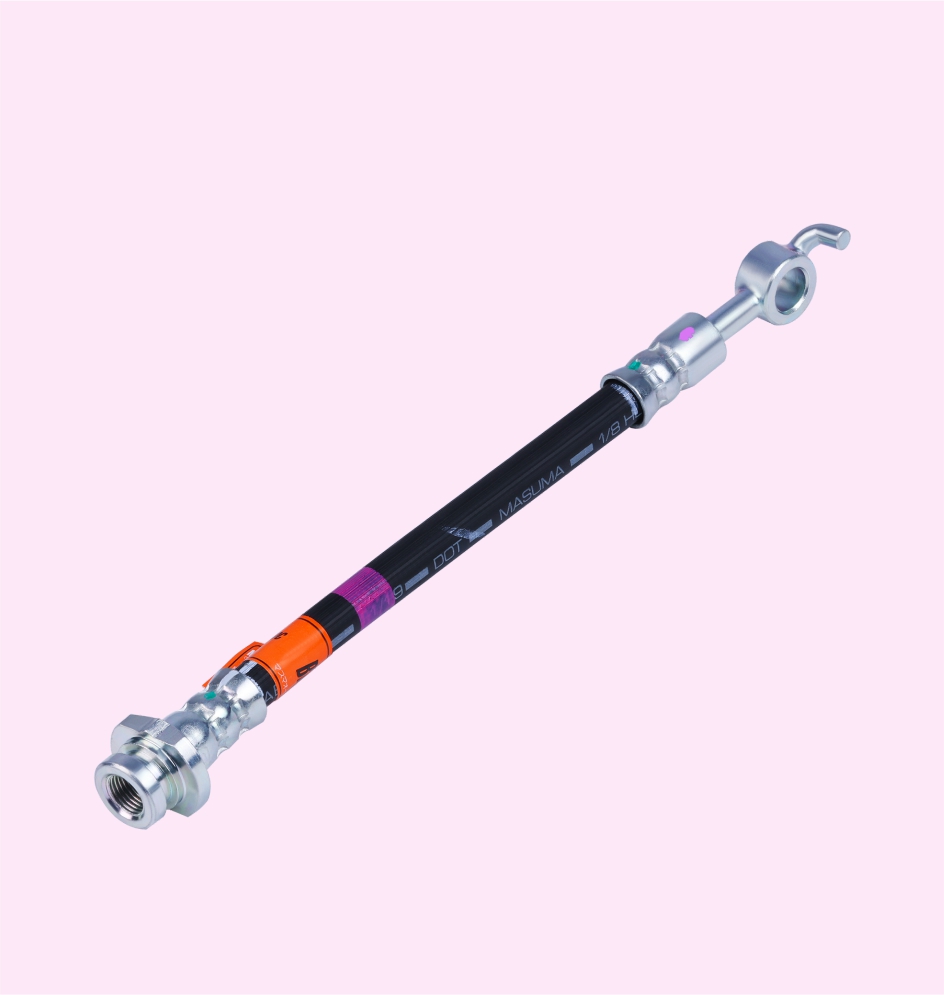
BRAKE HOSE
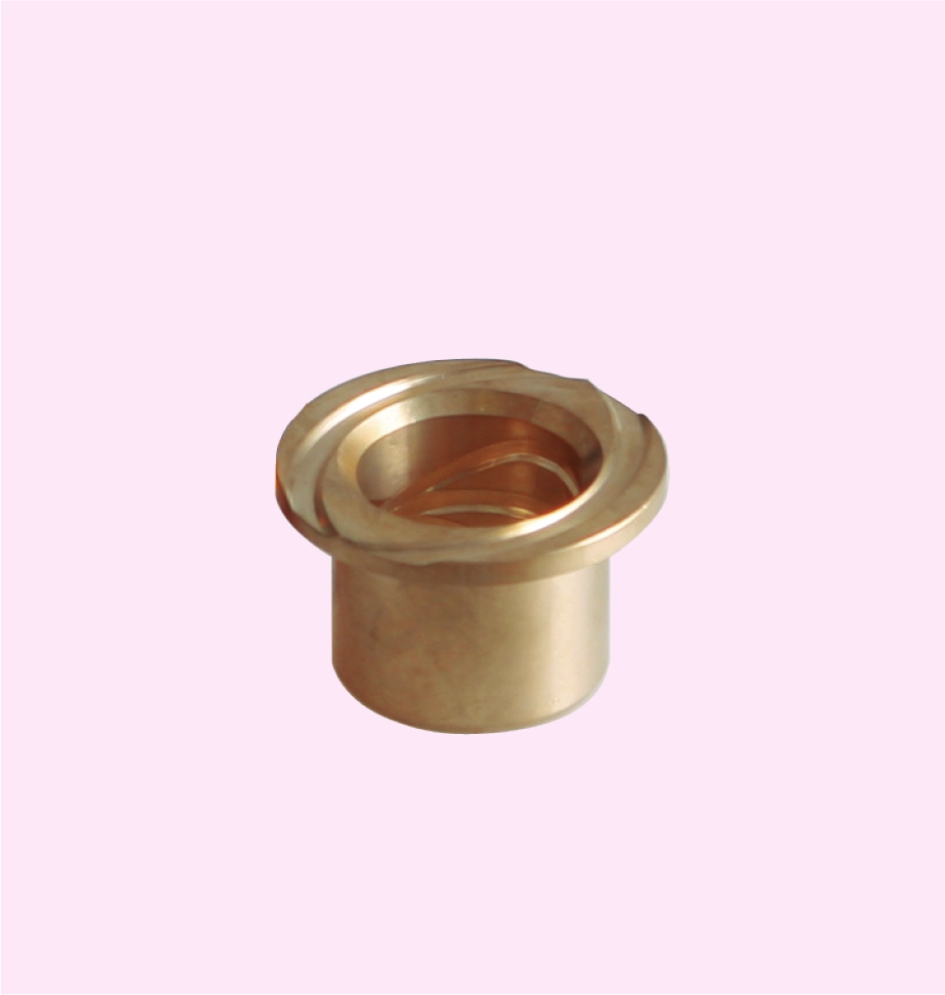
BRASS BUSHES (FOR STEERING KNUCKLE)
BELT TENSIONER IDLER
TIMING CHAIN KIT
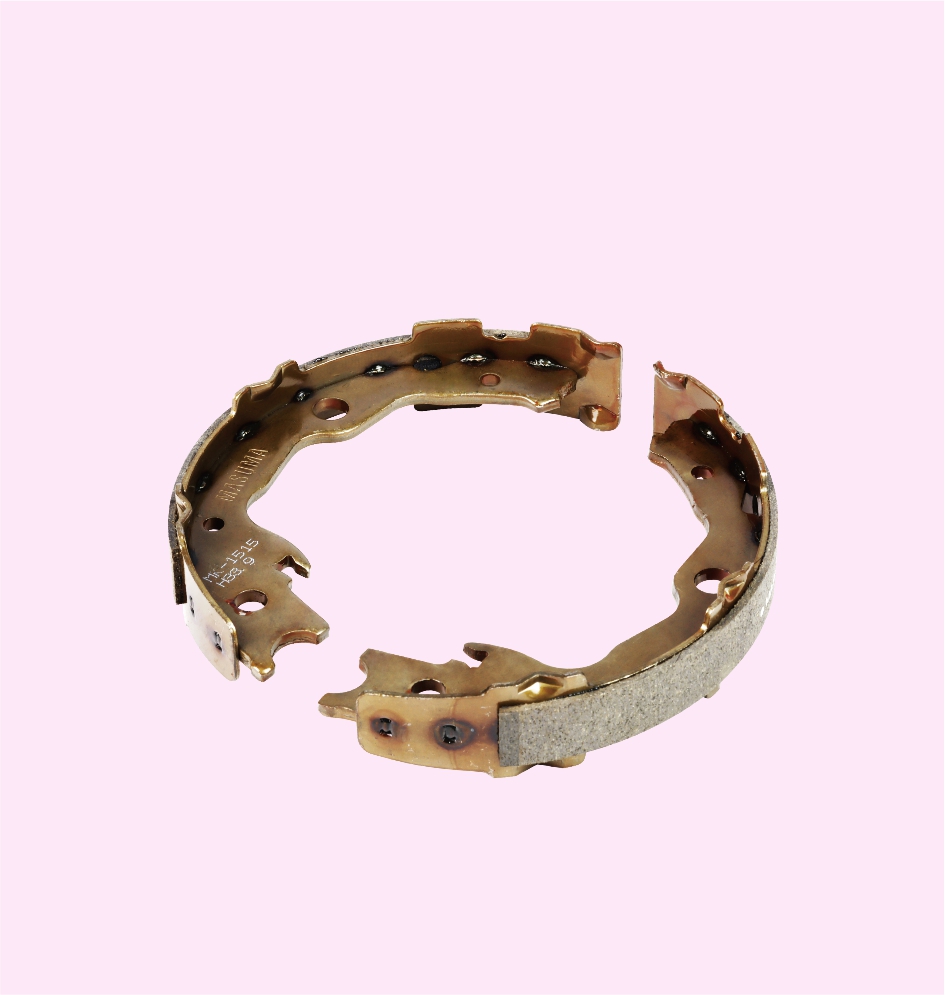
BRAKE SHOE
THERMOSTAT GASKET
VALVE COVER GASKET
AUTOMOTIVE RUBBER PARTS
WHEEL HUB UNIT
COIL SPRING
DISC BRAKE PADS
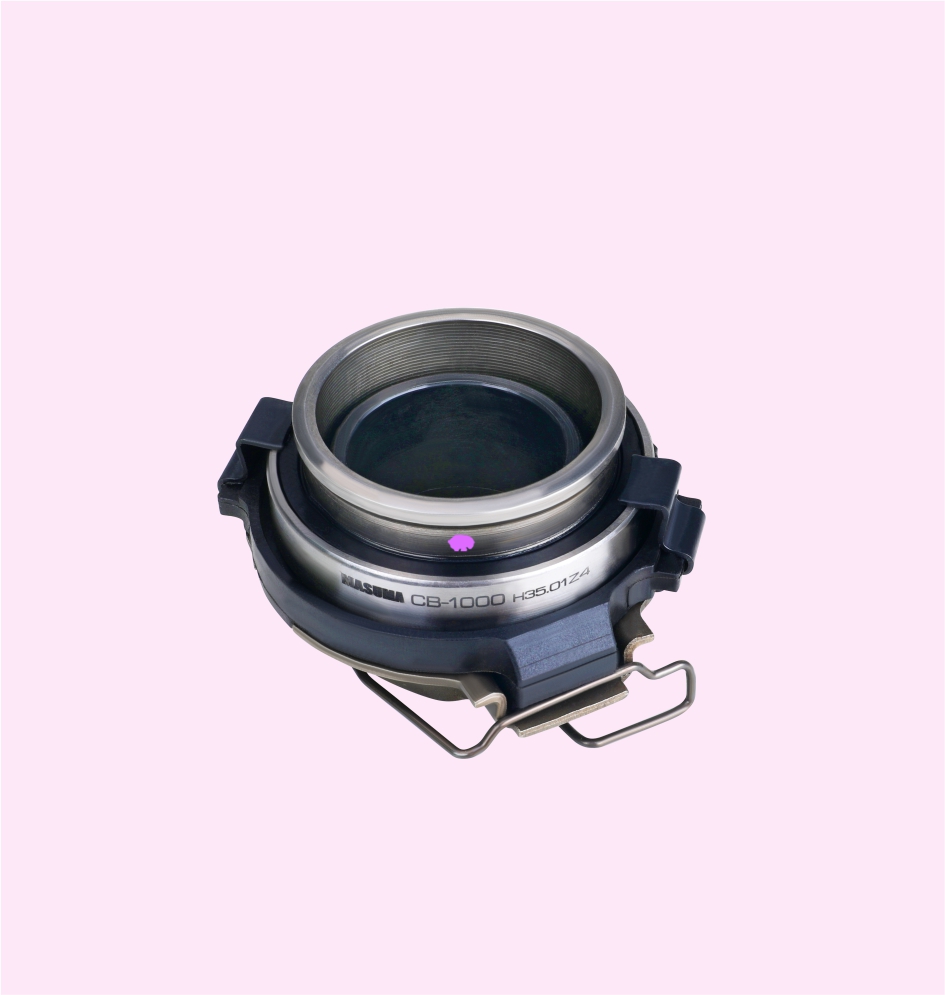
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING
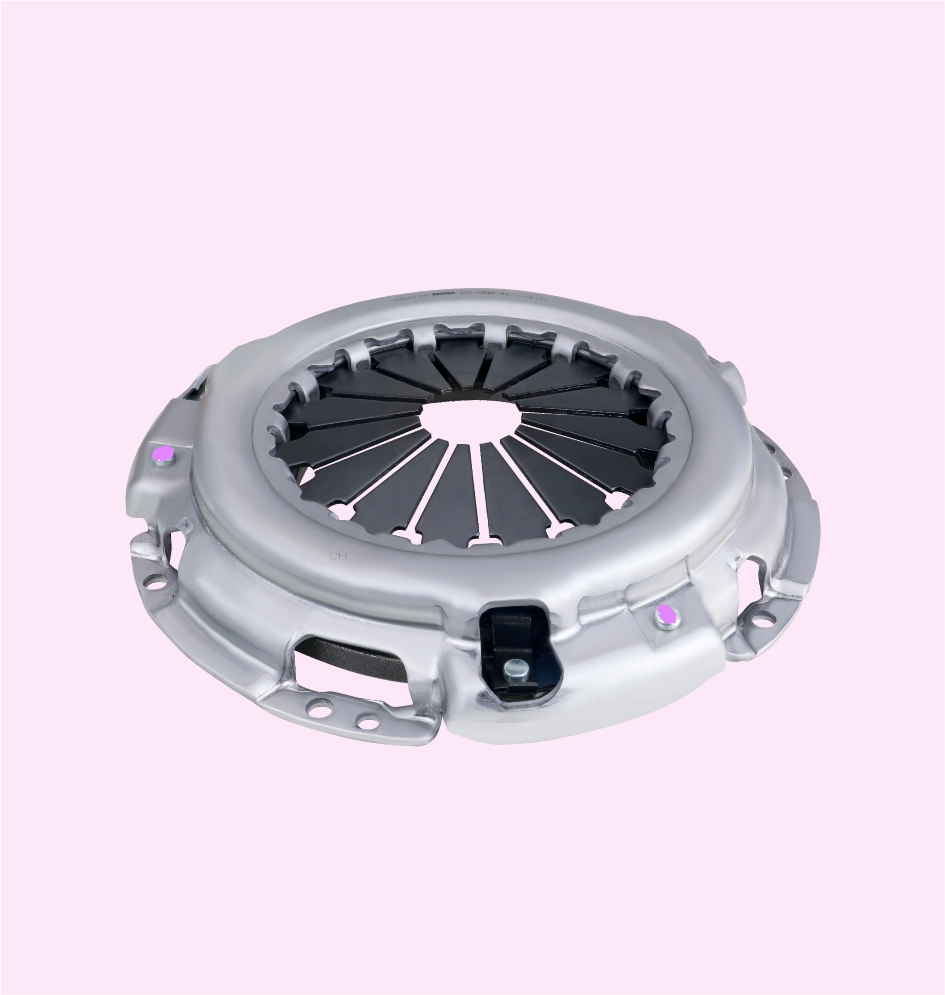
CLUTCH COVER
AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR
FUEL PUMP ASSEMBLY
BEARING SHOCK MOUNTING
OIL SEAL
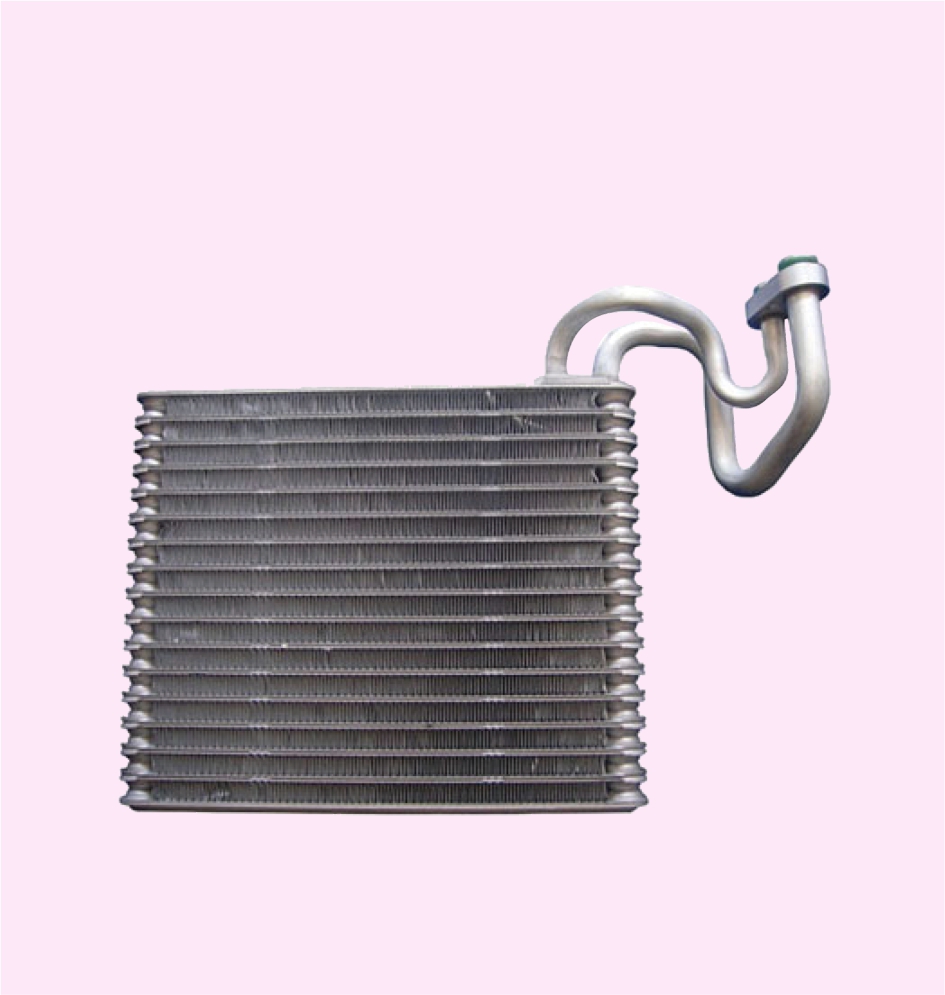
CONDENSER
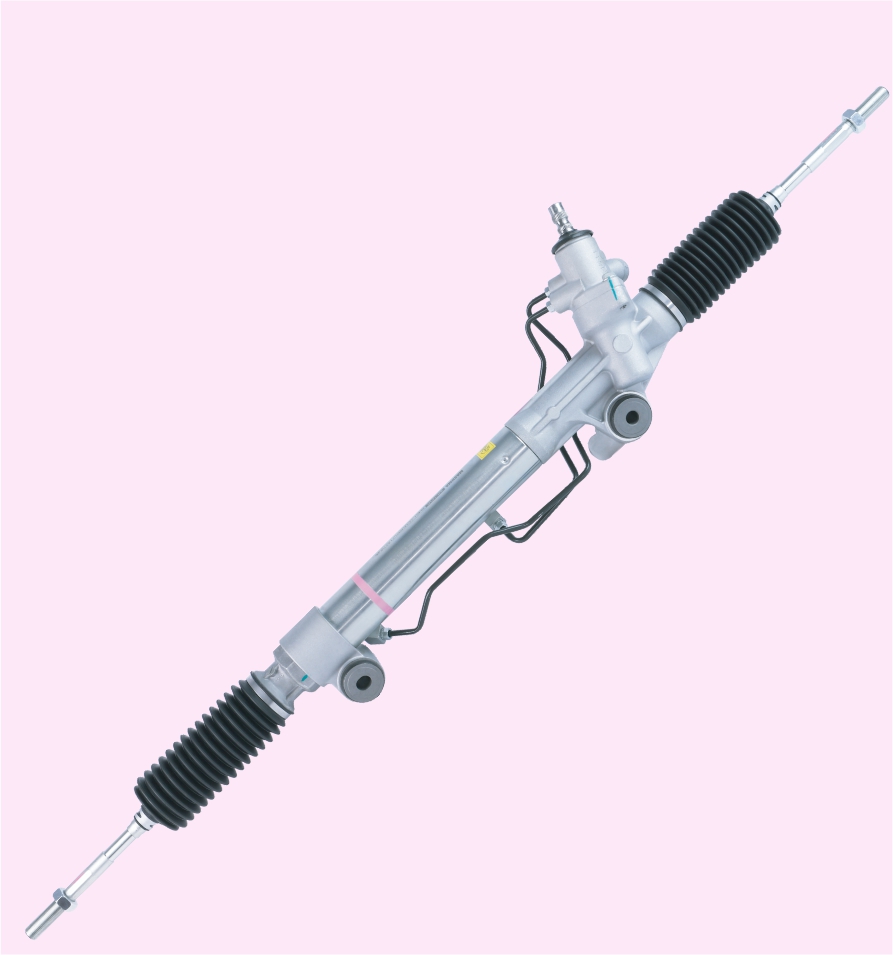
STEERING RACK
FUEL PUMP
CAP ASSY FUEL FILTER
WHEEL HUB BEARING
CV JOINT BOOT CLAMP KIT
HYDRAULIC FILTER
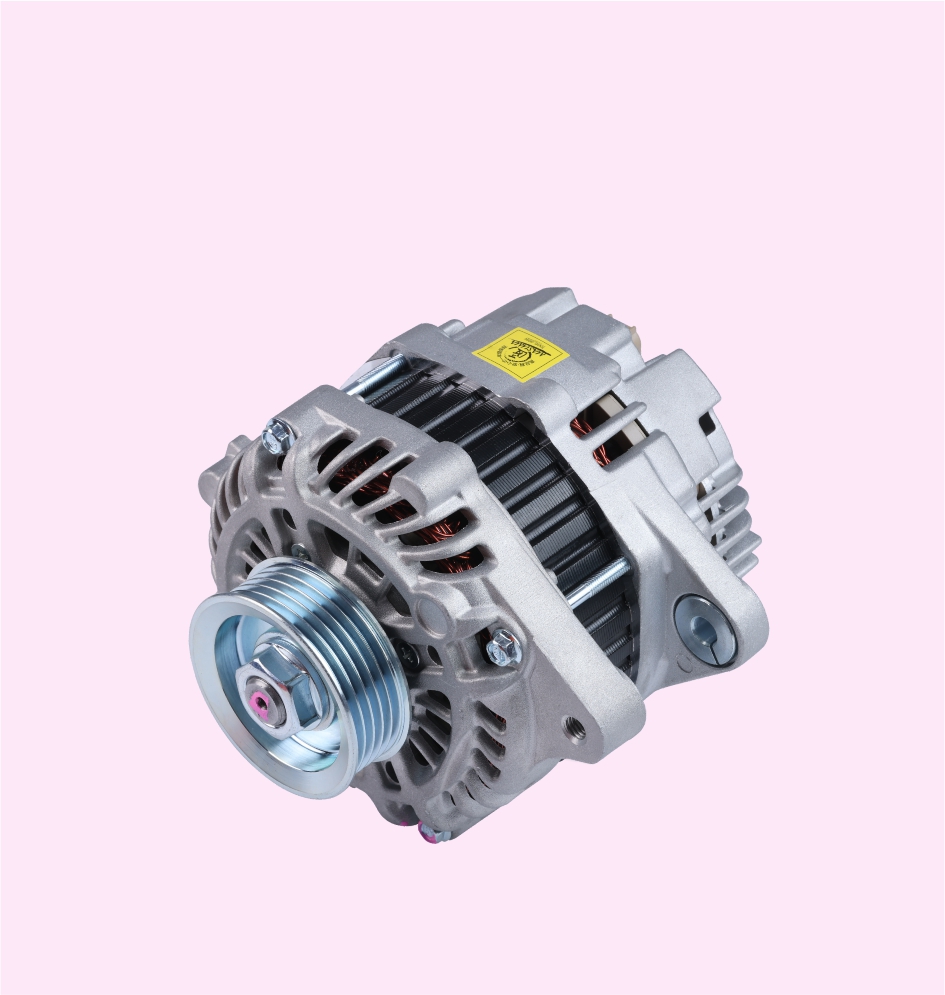
ALTERNATOR
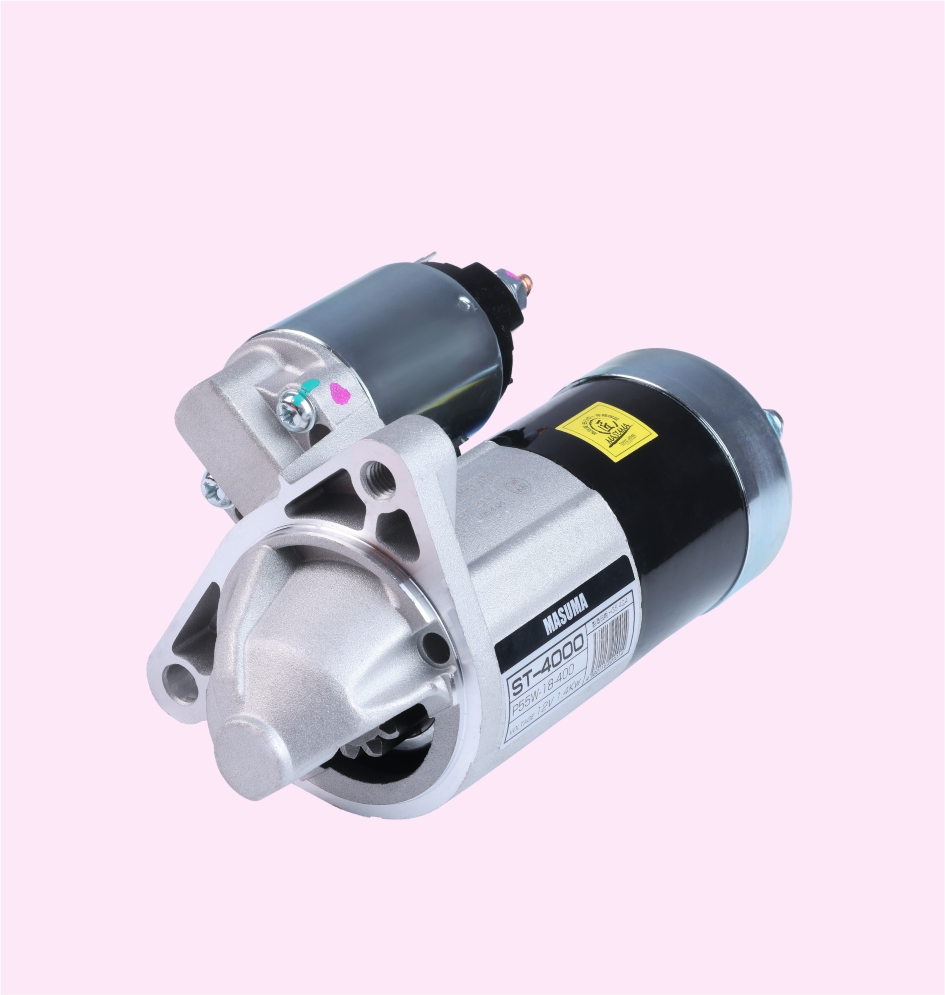
STARTER MOTOR
WATER PUMP/ELECTRONIC WATER PUMP
SENSOR FUEL FILTER
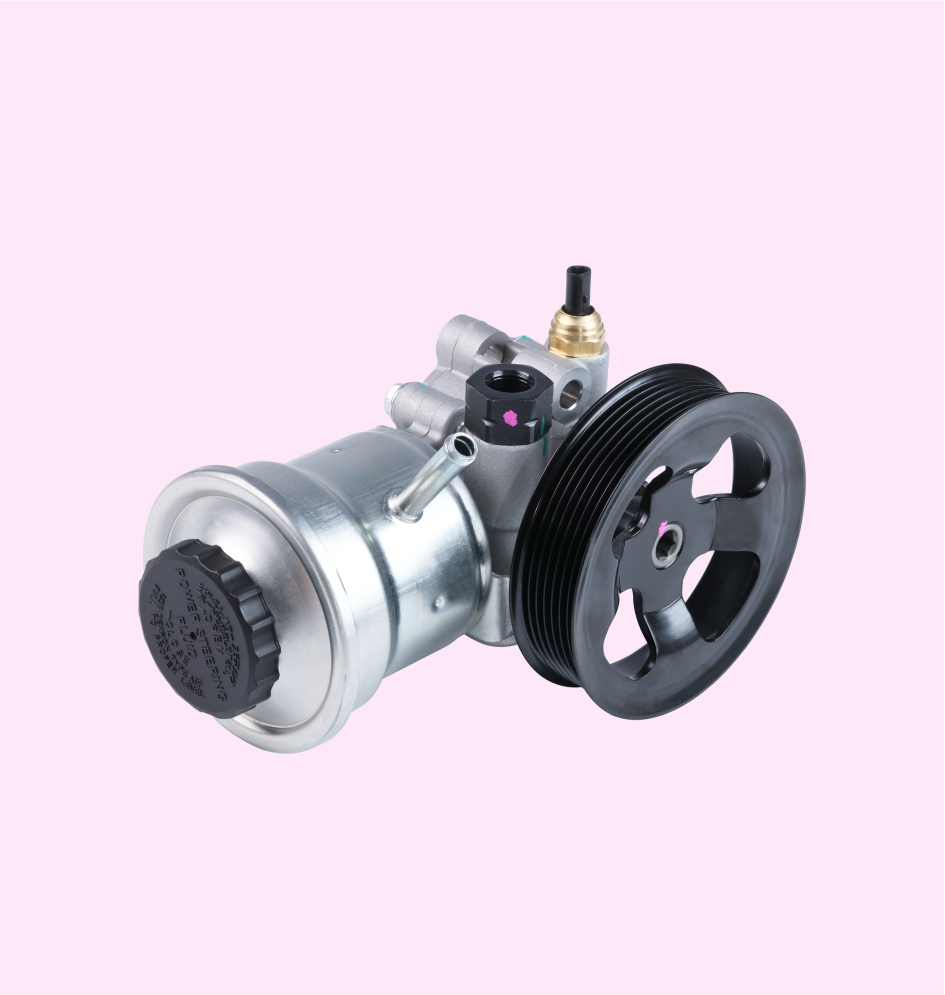
POWER STEERING PUMP
TIMING BELT
STRUT MOUNT
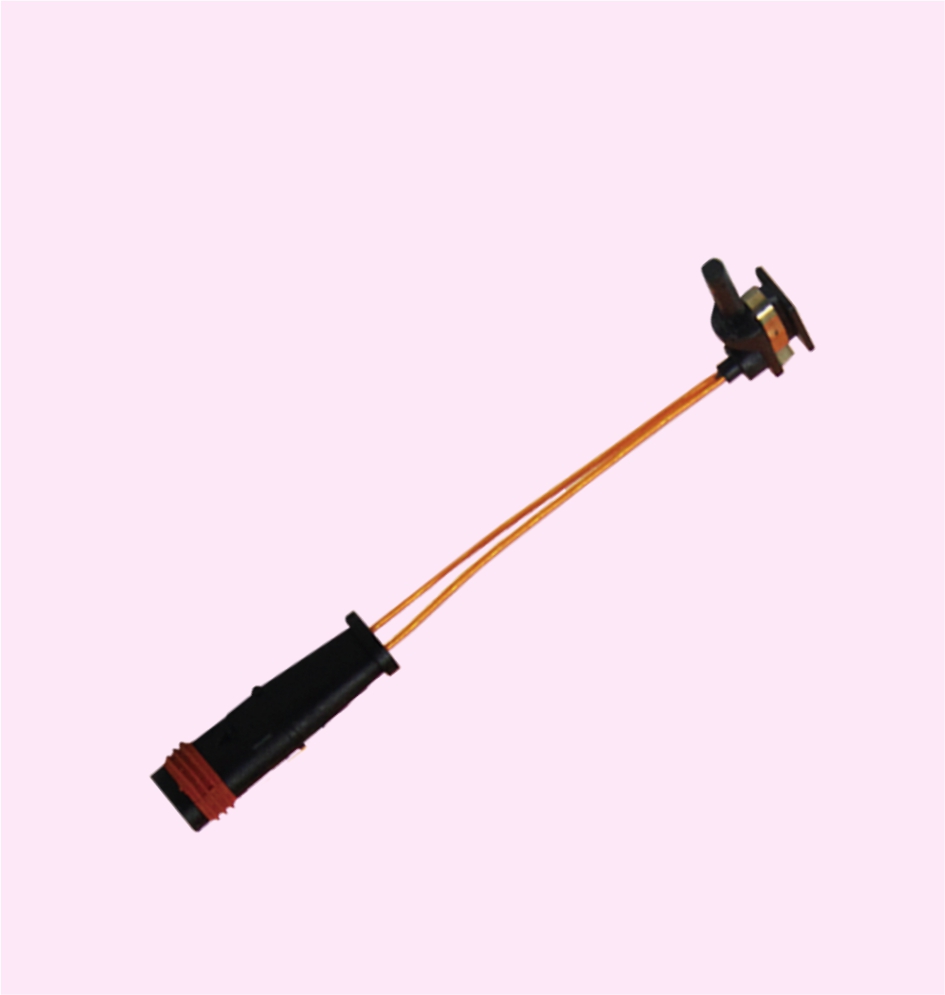
BRAKE PAD WEAR SENSOR
AIR FILTER
OIL FILTER
FUEL FILTER
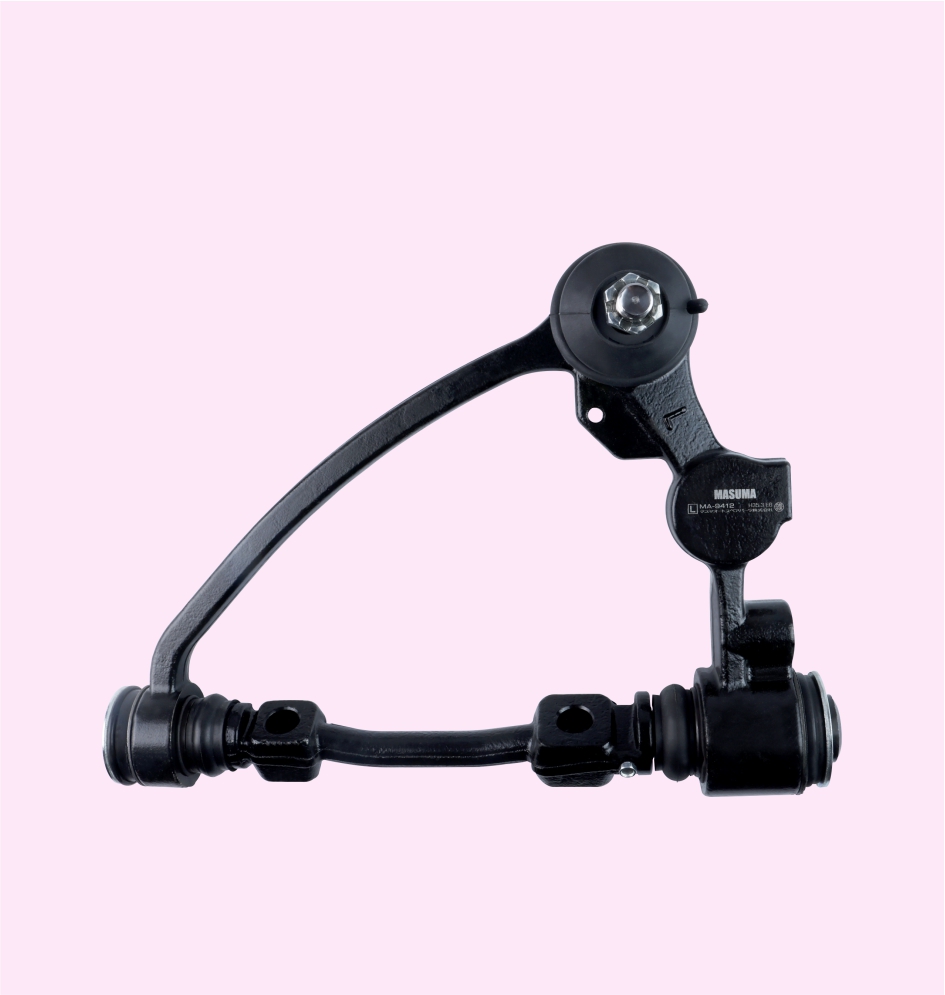
CONTROL ARM
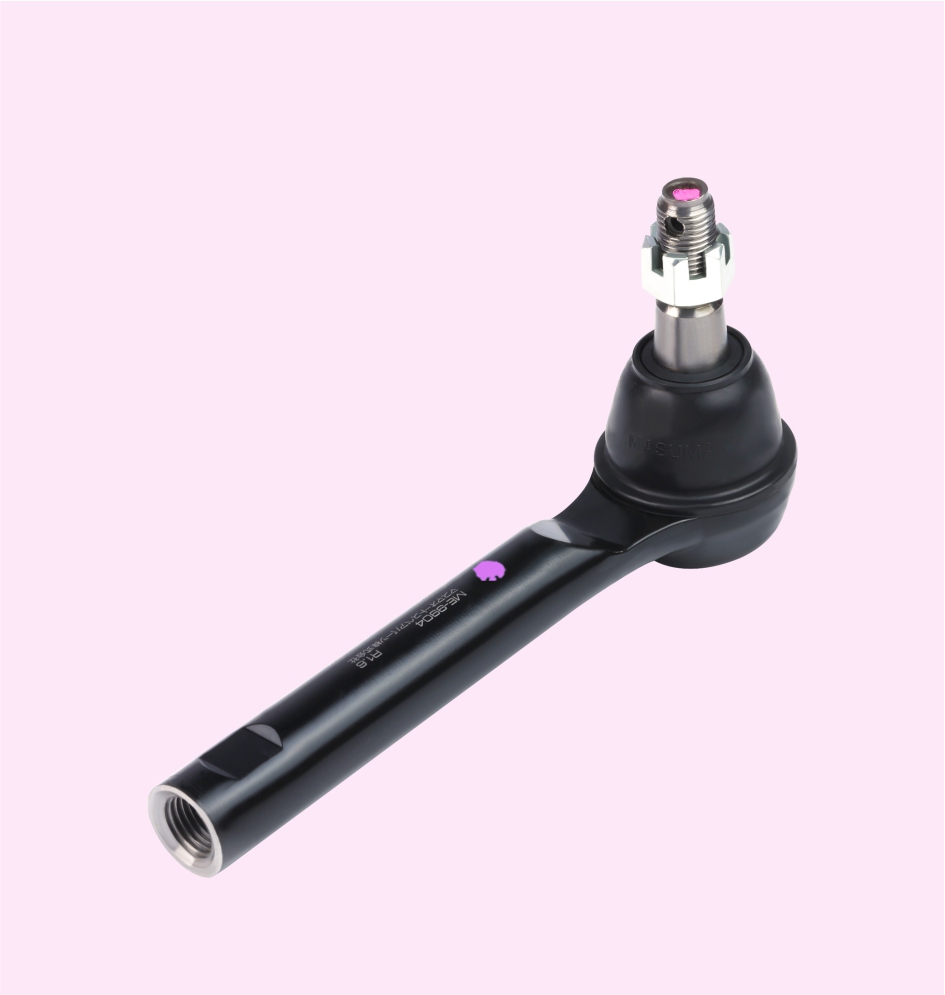
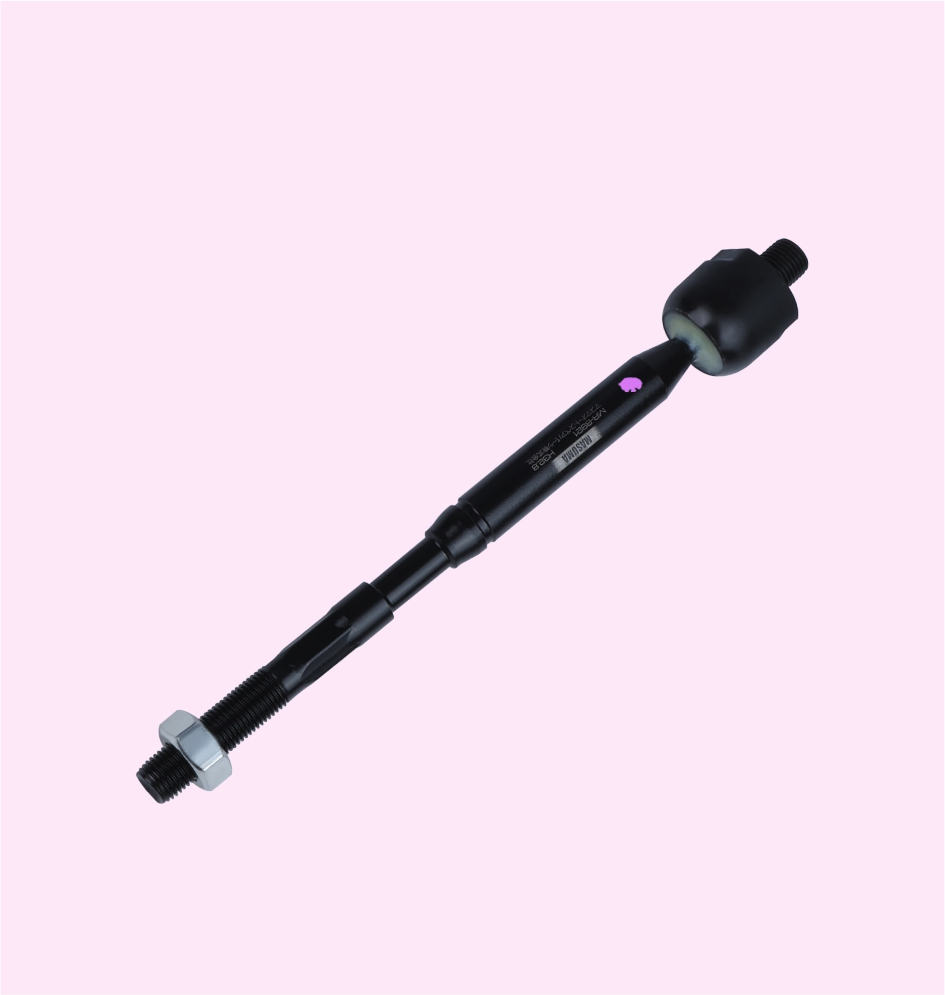
RACK END
TIE ROD END
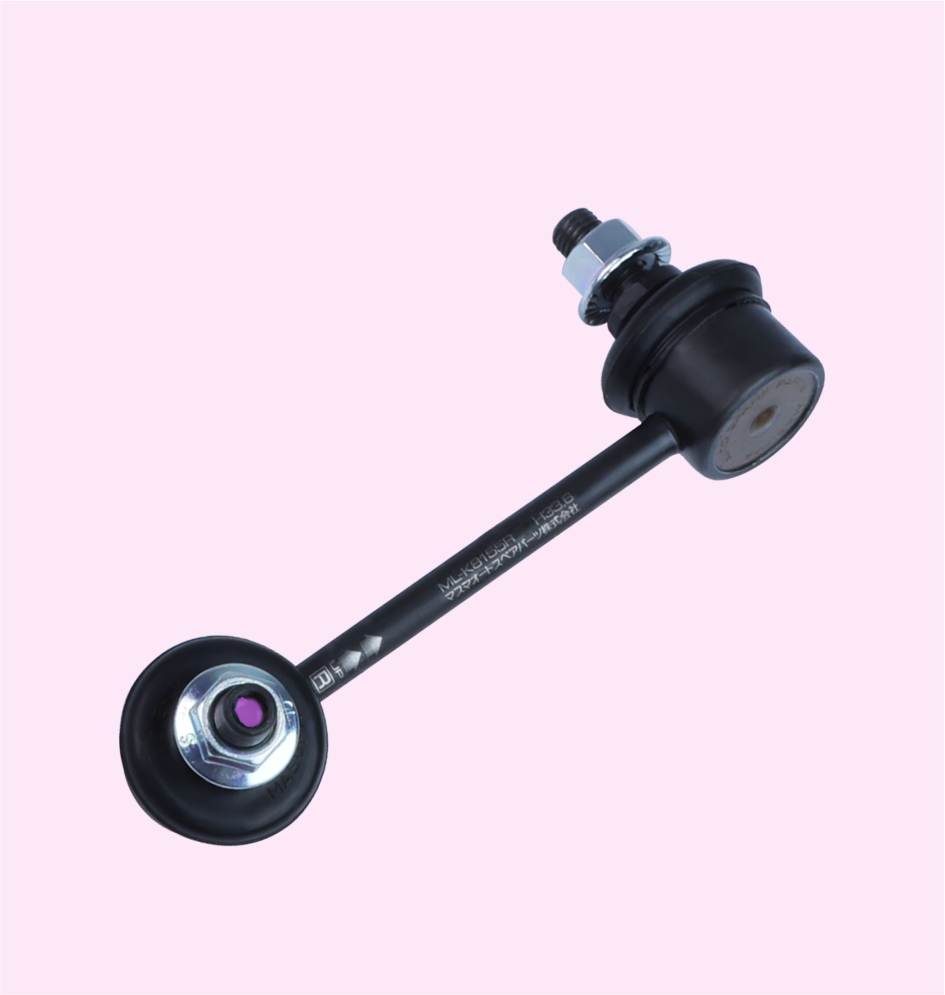
STABILIZER LINK
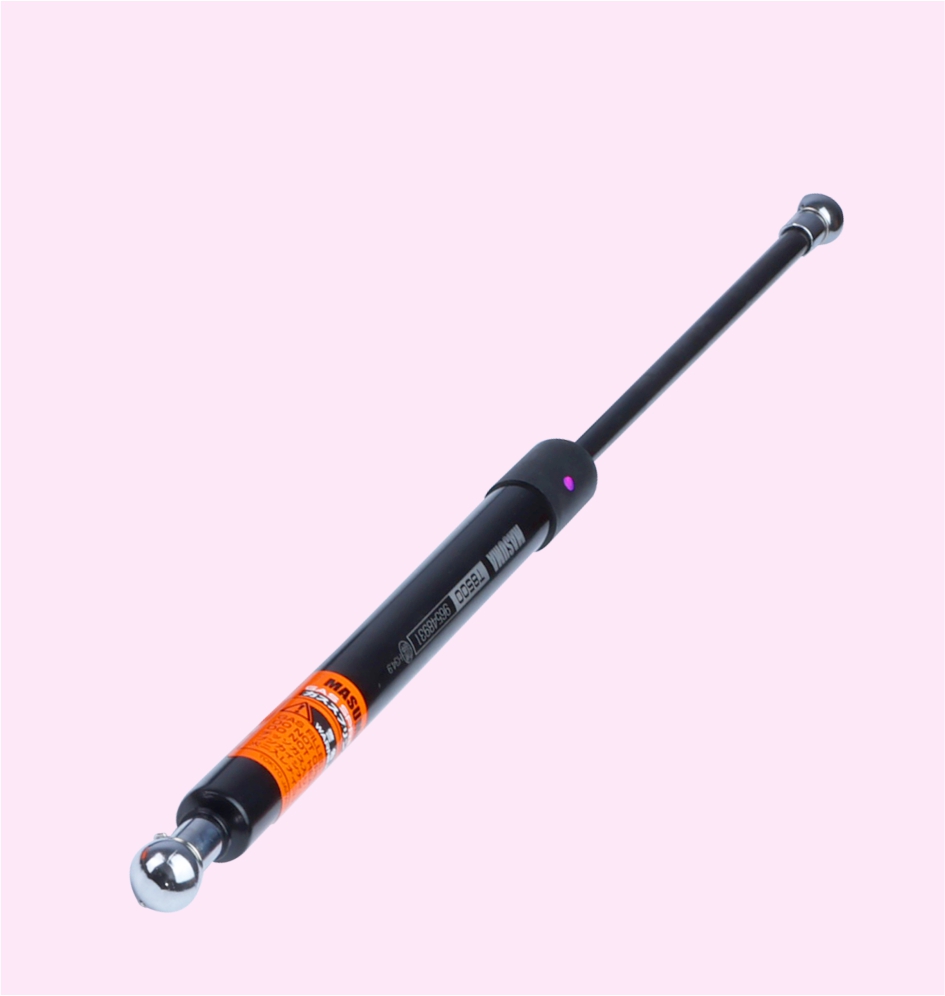
GAS SPRING
BALL JOINT DUST COVER
TRANSMISSION FILTER
AUTOMOTIVE CLIPS & FASTENERS
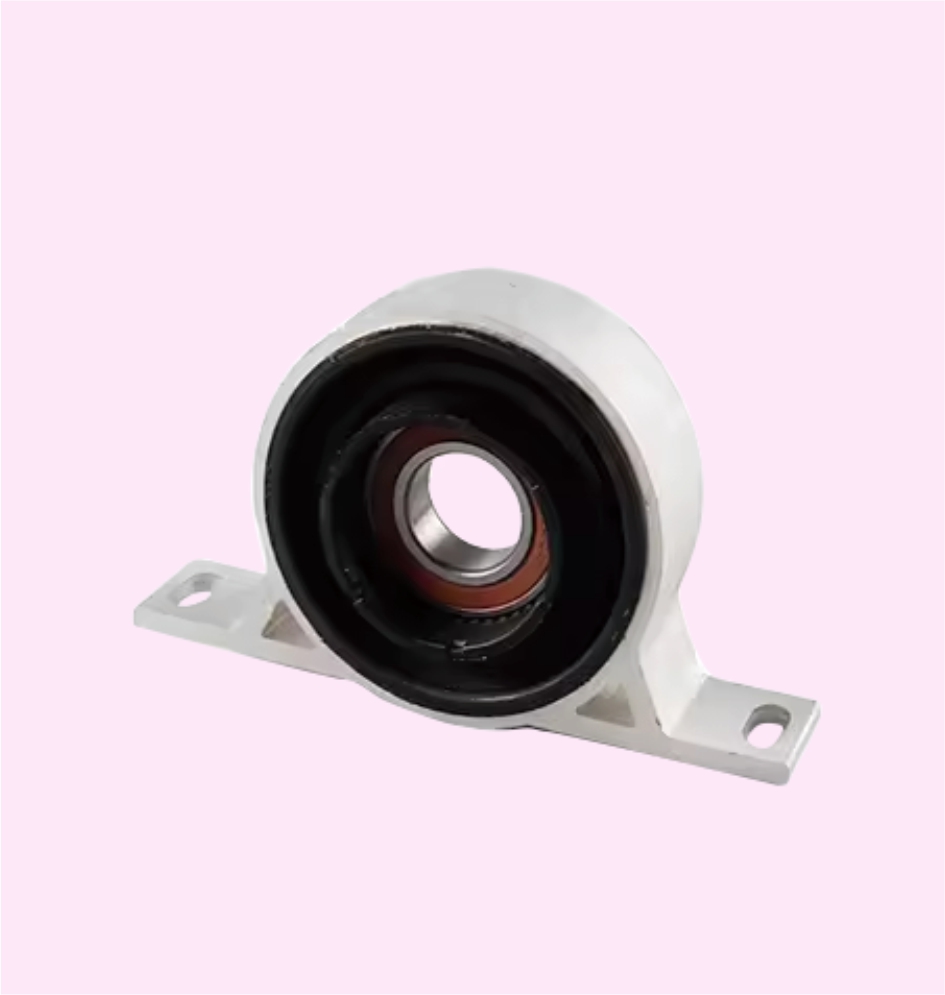
CENTER SUPPORT BEARINGS
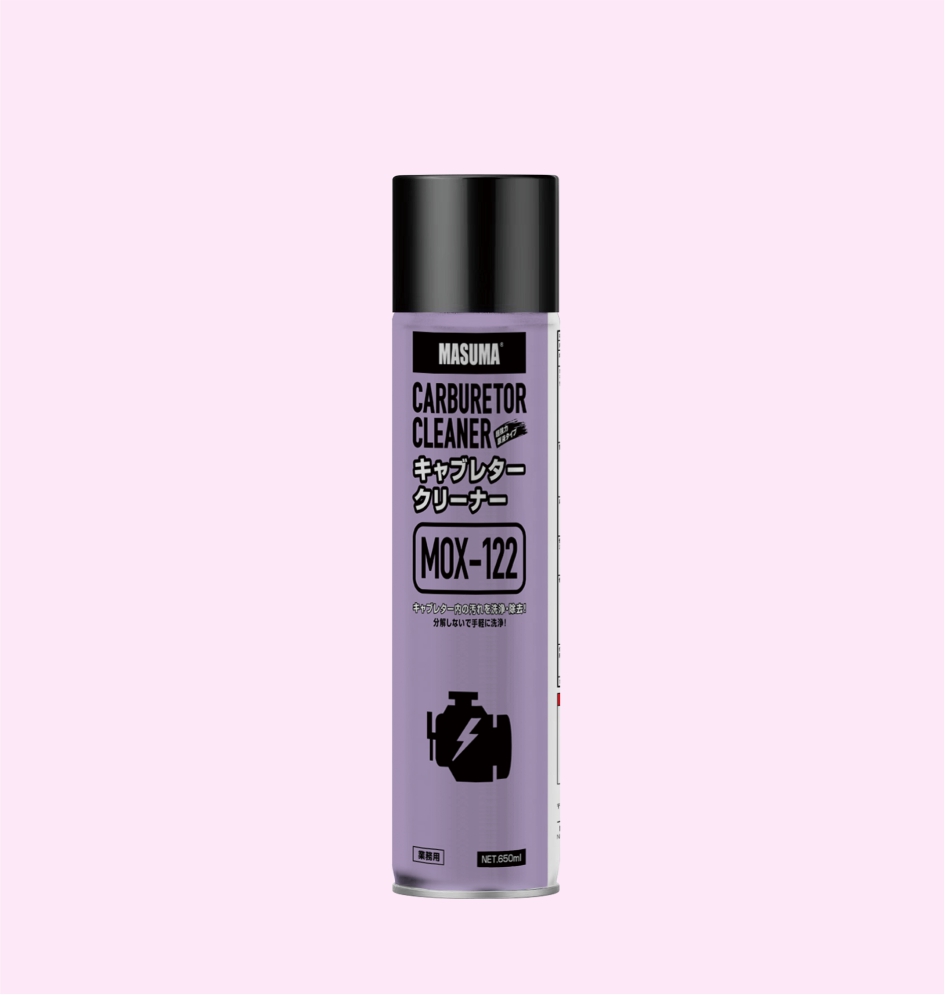
CARBURETOR CLEANER
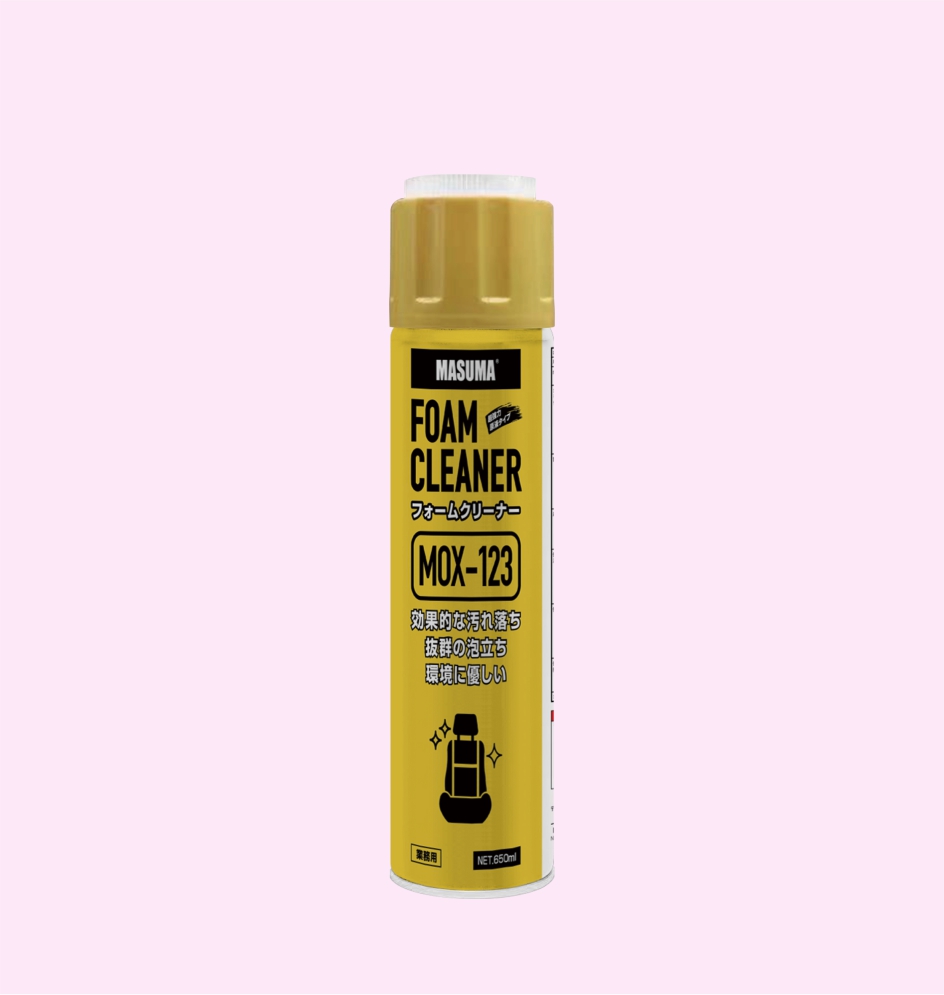
FOAM CLEANER
SILICONE SPRAY
PITCH CLEANER
MOTOR FLUSH
TRIM & PLASTIC RESTORER
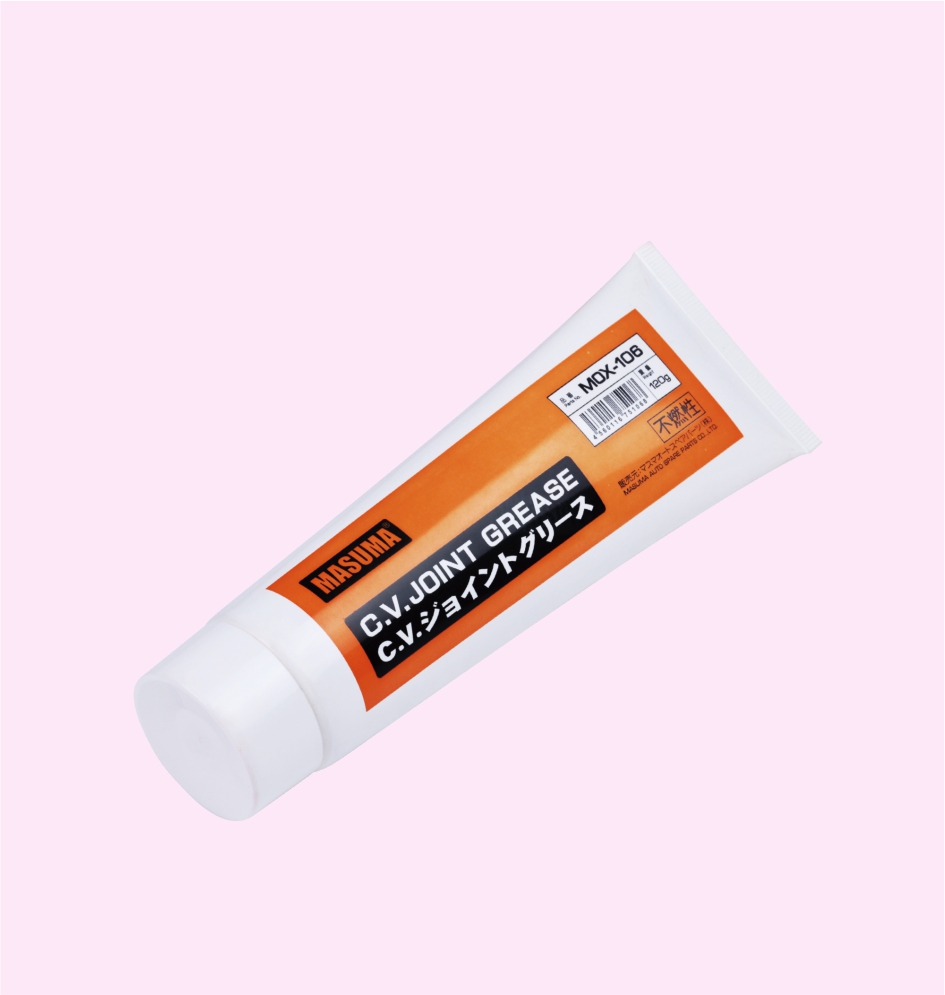
C .V. JOINT GREASE
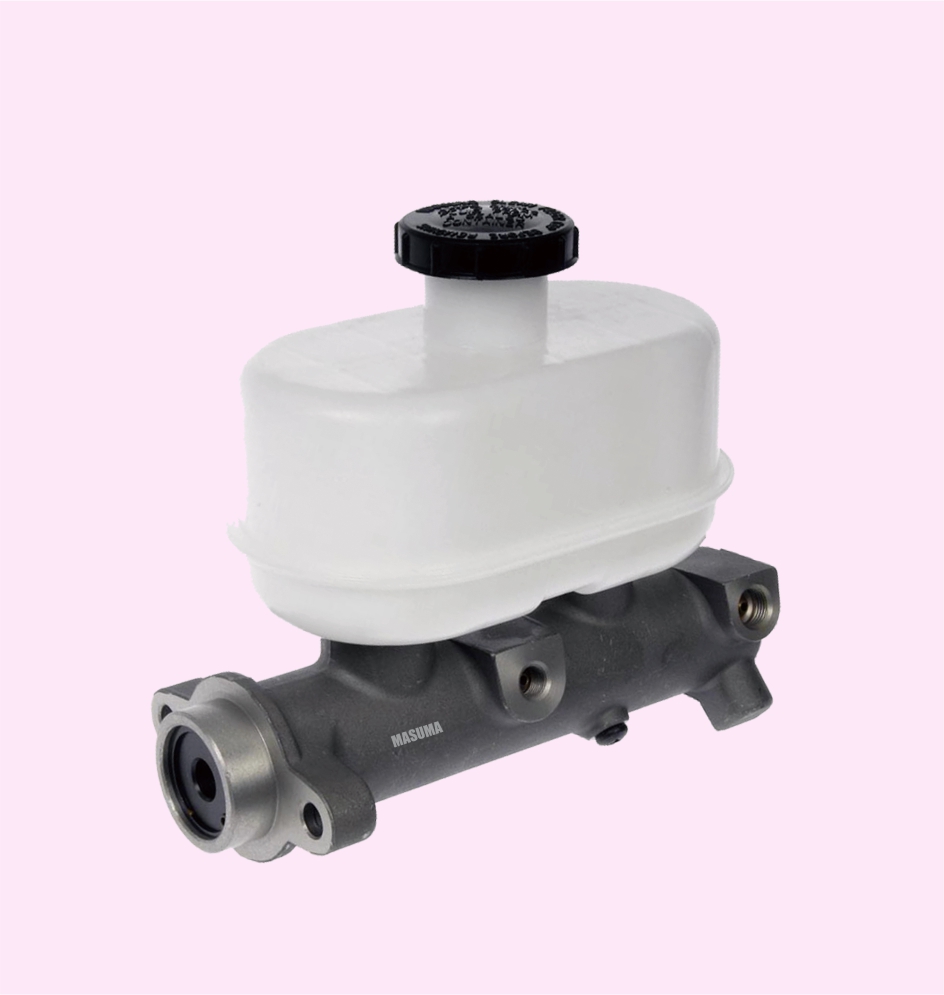
BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER
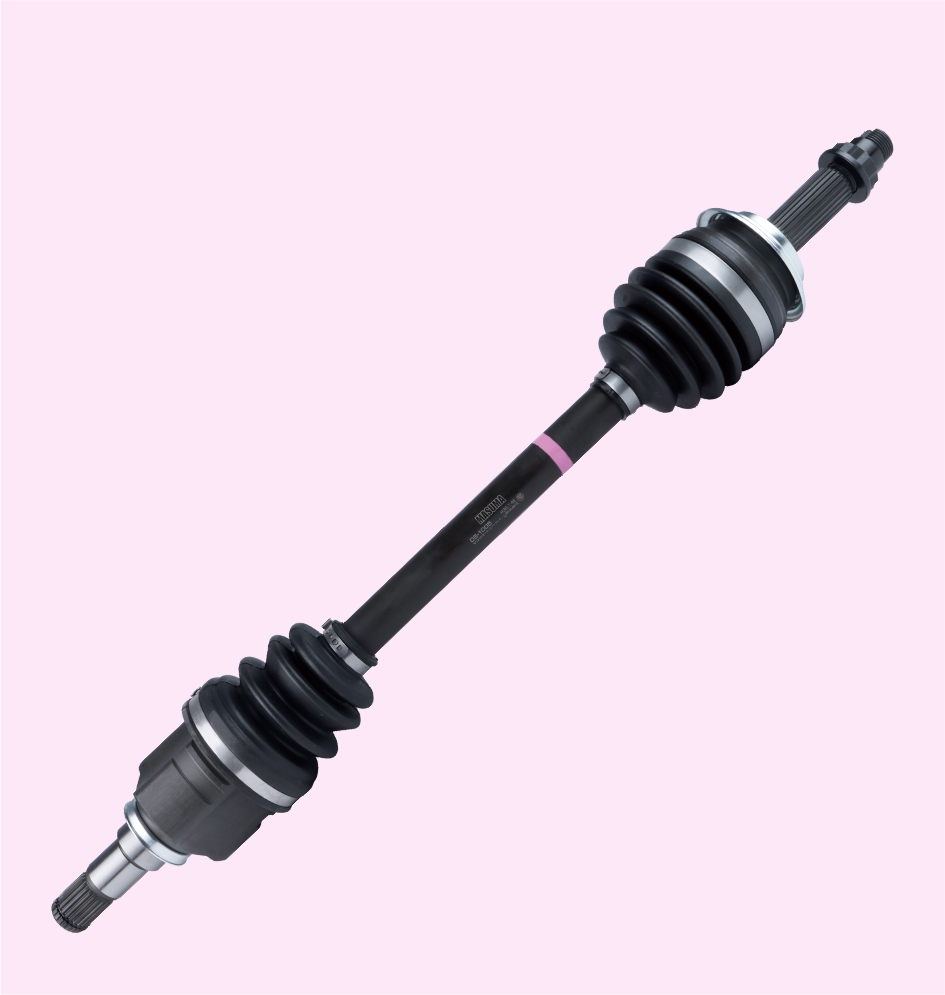
DRIVE SHAFT
MF BATTERY
FUEL INJECTOR
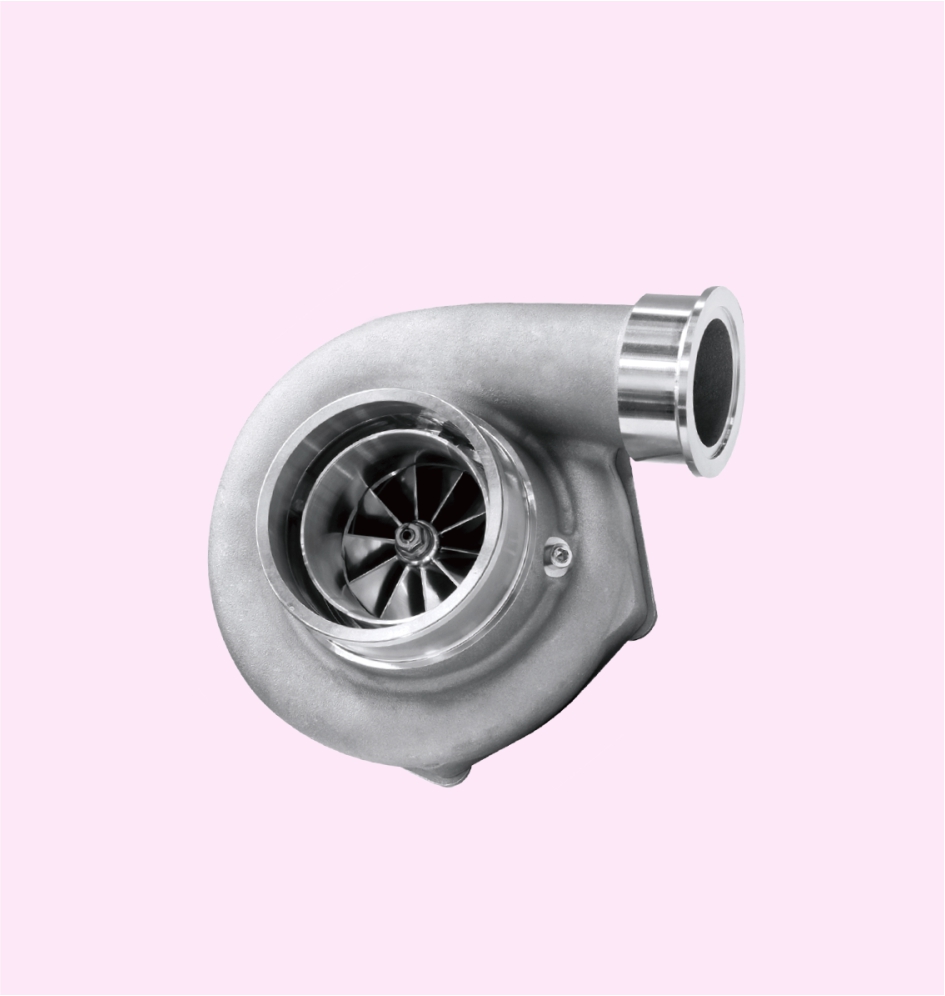
TURBOCHARGER
FUEL TANK CAP
CAM PHASER
V-BELT
DRAIN BOLT
V-RIBBED BELT
TIRE REPAIR PLUG
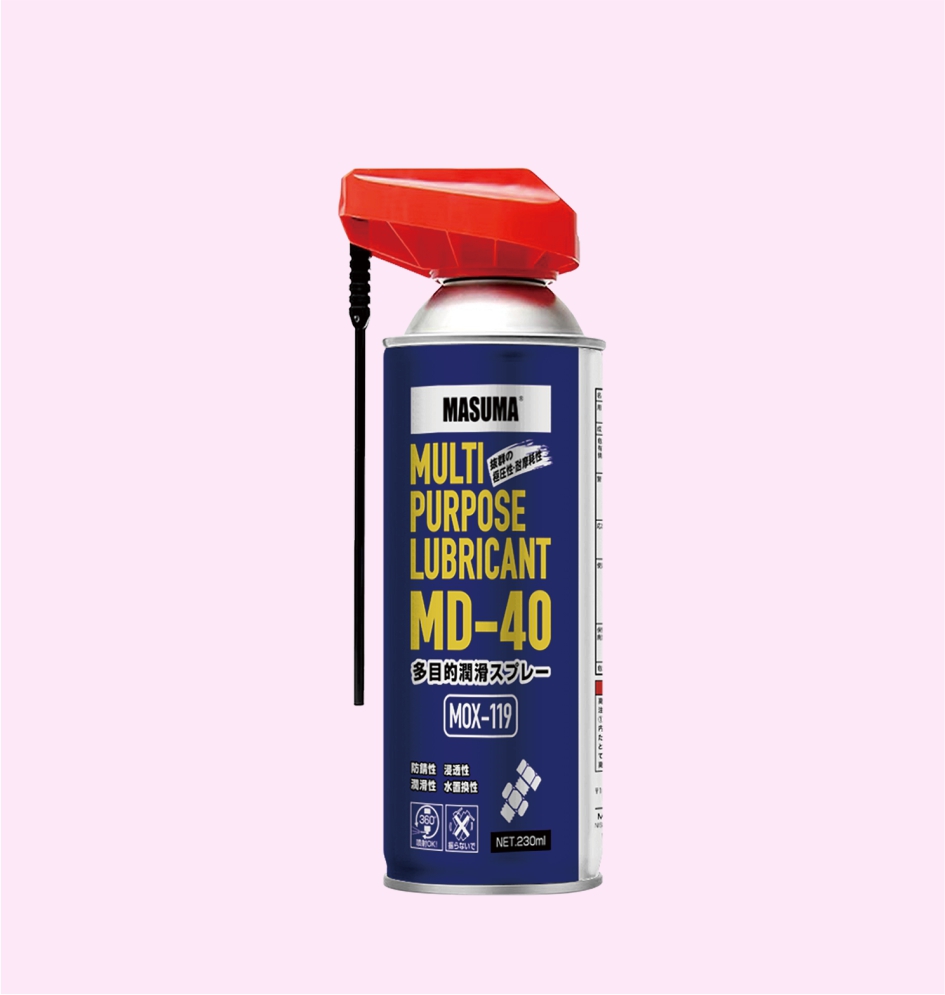
MULTI-PURPOSE LUBRICANT
DISK BRAKE ANTI-SQUEAL GREASE
BRAKE CLEANER KIT
PROPELLER SHAFT
RADIATOR DRAIN COCK
THERMO SWITCH
GRAPHITE GASKET
WIPER RUBBER
HORN
RADIATOR CAP
BRAKE CYLINDER GREASE
WIPER BLADE ADAPTER
AUTO EXHAUST FLEXIBLE PIPE
SPHERICAL JOINTS PIPE
WIPER BLADE DISPLAY STAND
DISPLAY STAND
OIL QUALITY COMPARATOR
SPARK PLUG TESTER
OIL FILTER CUTTER
POLO SHIRT
T-SHIRT (ORANGE)
T-SHIRT (BLACK)
JACKET
OVERALLS
COVERALLS
REFLECTIVE VEST
BASEBALL CAP(BLACK)
BASEBALL CAP (ORANGE)
13G POLYESTER LATEX COATD GLOVES
UMBRELLA
BACKPACK
MOUSE PAD
THROW PILLOW
COMPANY FLAG
WATER FILLED BANNER FLAG
PLASTIC BAG
FOLDER (SINGLE LAYER)
FOLDERS (MULTIPLE LAYERS)
ZIPPER FILE HOLDER
ELECTRIONIC QUARTZ CLOCK
WHEEL HUB WATCH
ASHTRAY
VACUUM THERMOS FLASK(BLUE)
SQUARE LIGHT BOX SIGNAGE
AIR FRESHENER
ADVERTISING STICKERS
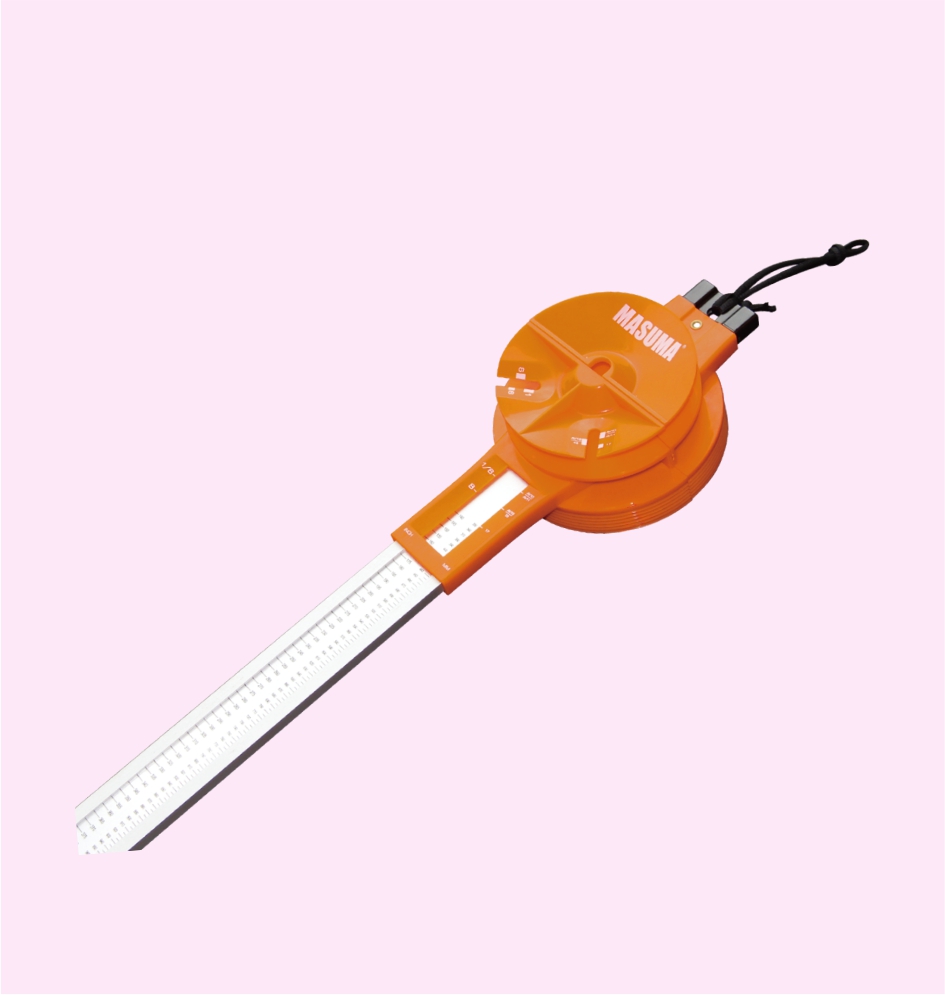
BELT MEASURING GAUGE
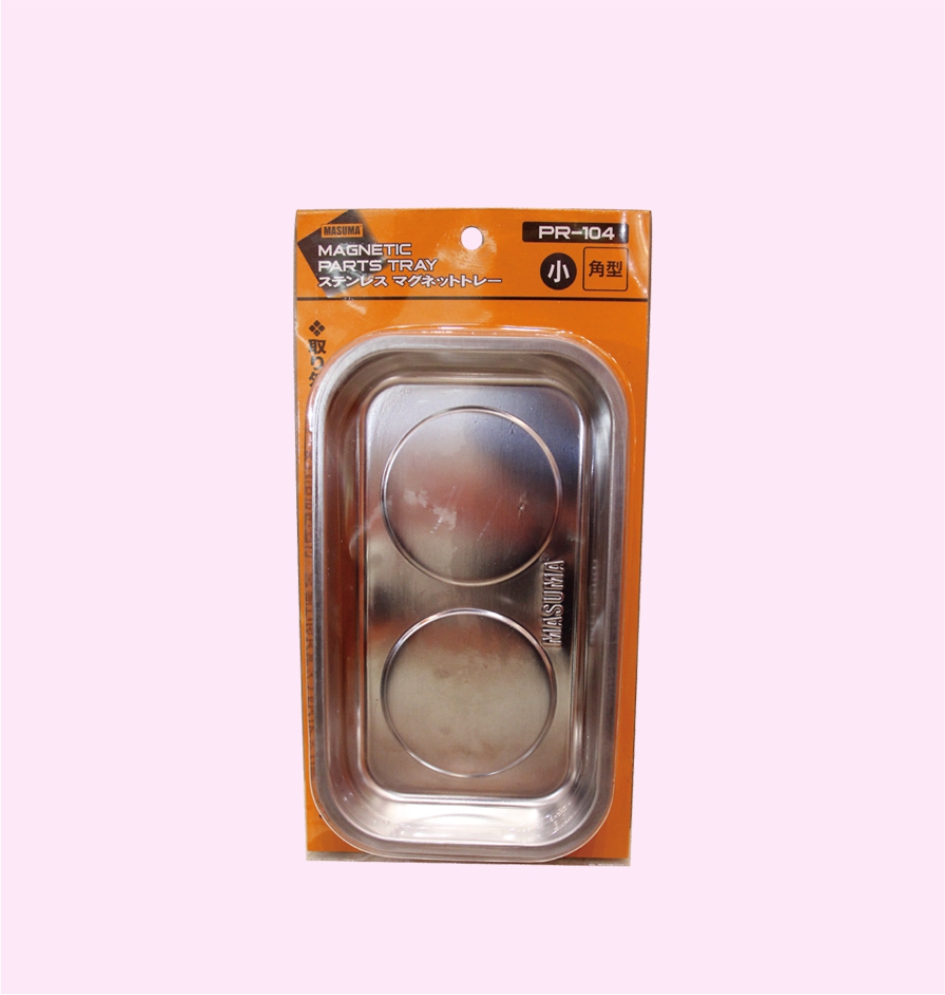
MAGNETIC PARTS TRAY
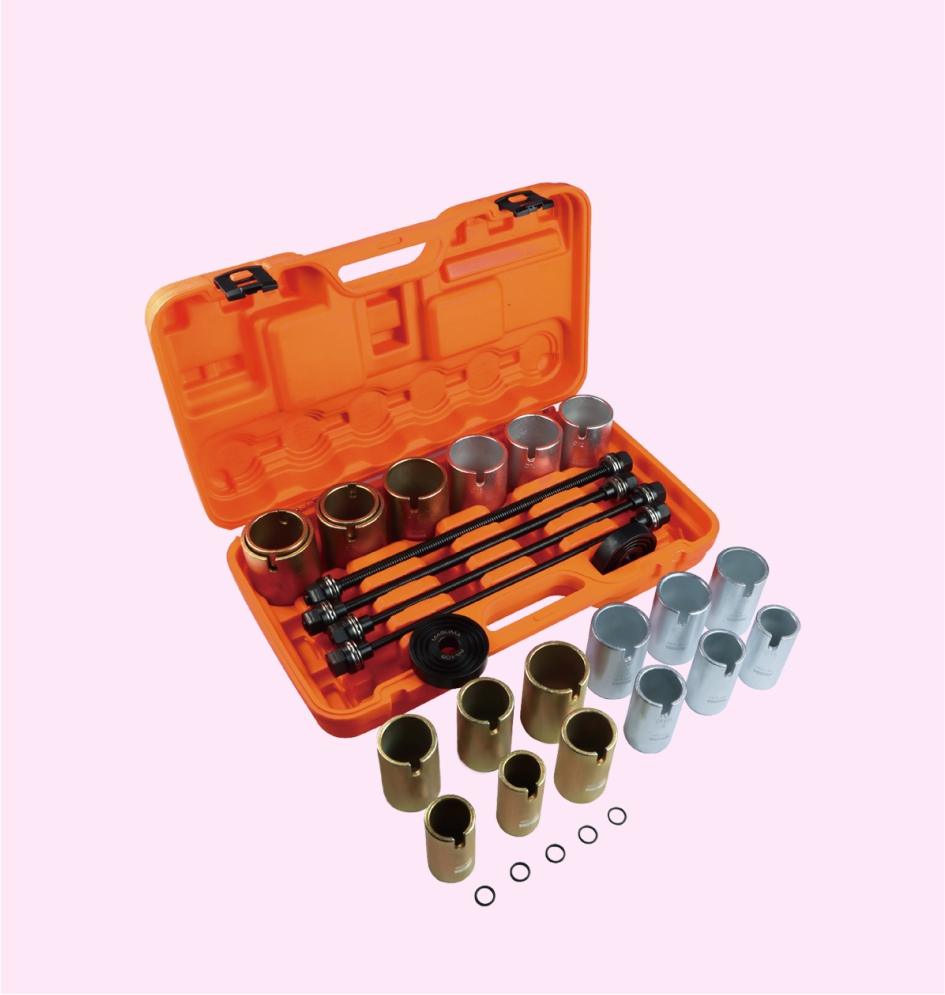
BUSHING REMOVAL & INSTALLATION TOOL KIT
BRAKE WHEEL CYLINDER REPLACEMENT TOOL
MECHANICS CREEPER
CREEPER SEAT
DISPOSABLE CAR SEAT COVER
DISPOSABLE STEERING WHEEL COVER
DISPOSABLE FLOOR MATS
BRAKE FLUID FLUSH & EXCHANGE MACHINE
COOLANT FLUSH & EXCHANGE MACHINE
TRANSMISSION FLUID FLUSH & EXCHANGE MACHINE
TRANSMISSION FLUID NOZZLE
A/C CHARGING HOSE
BRAKE DISC LATHE
BUSHING REMOVAL & INSTALLATION TOOL
MAGNETIC FENDER COVER WORK MAT
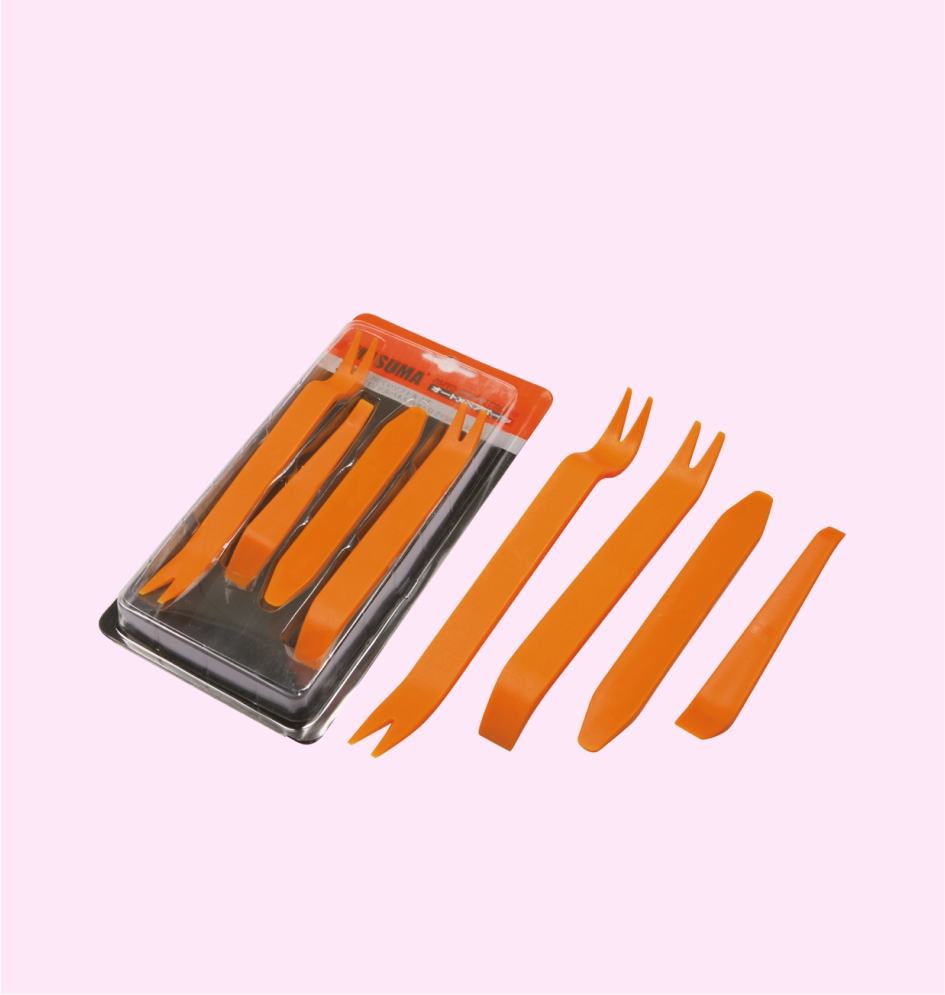
AUTO TRIM REMOVAL TOOL
HALOGEN BULB
LED BULBS
XENON HID BULB
C.V. JOINT NUT
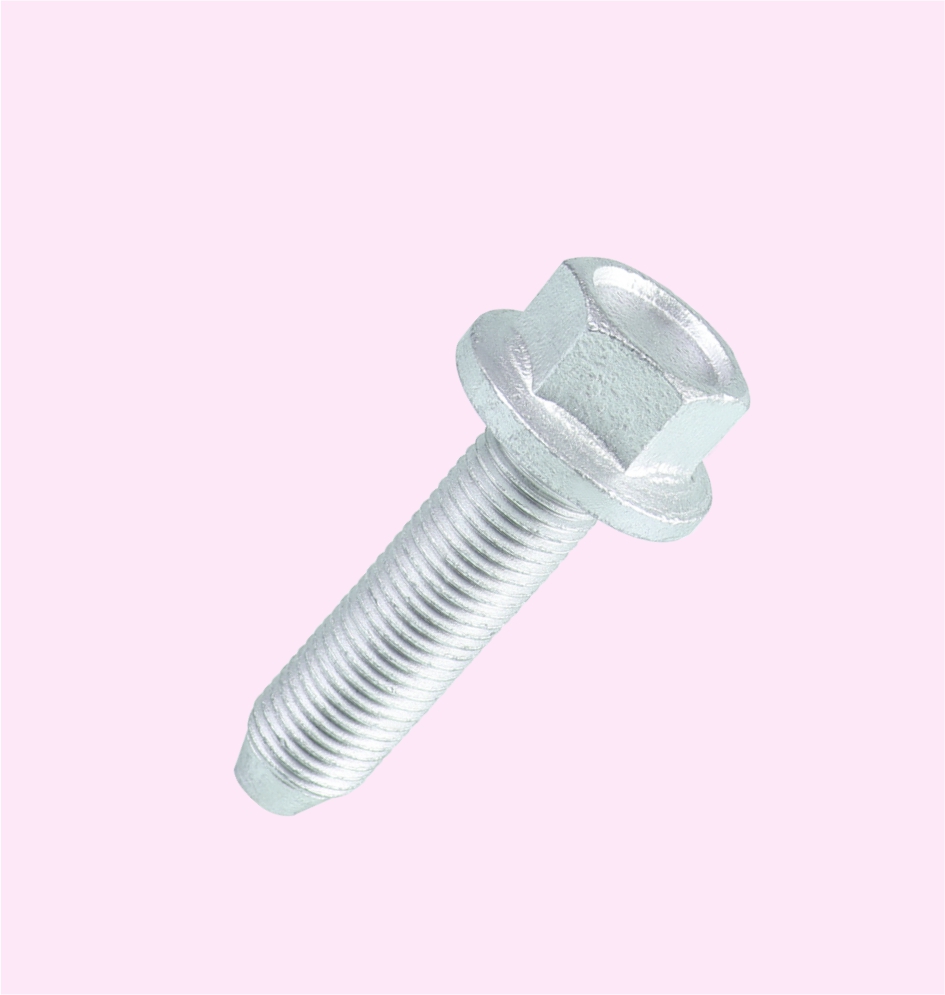
BRACKET BOLT
ECCENTRIC BOLT
TIMING BELT KIT
SHOCK ABSORBER DUST COVER
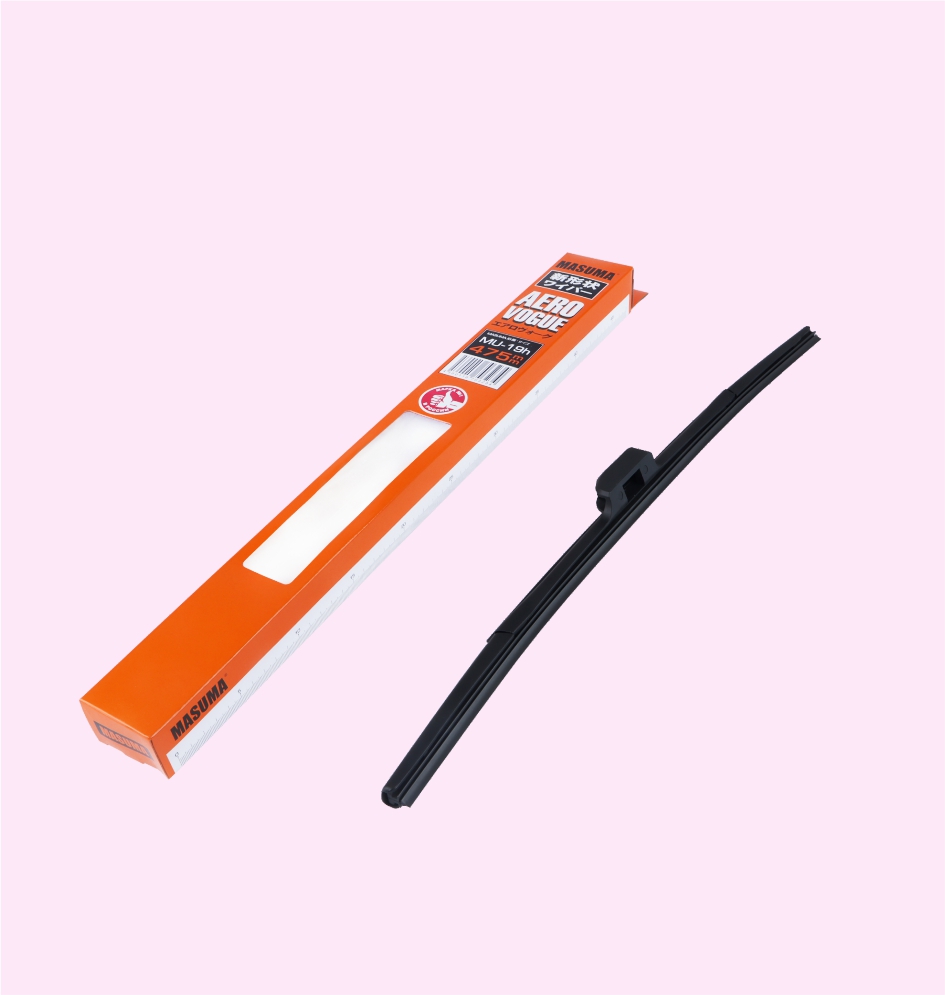
WIPER BLADE(NANO GRAPHITE)
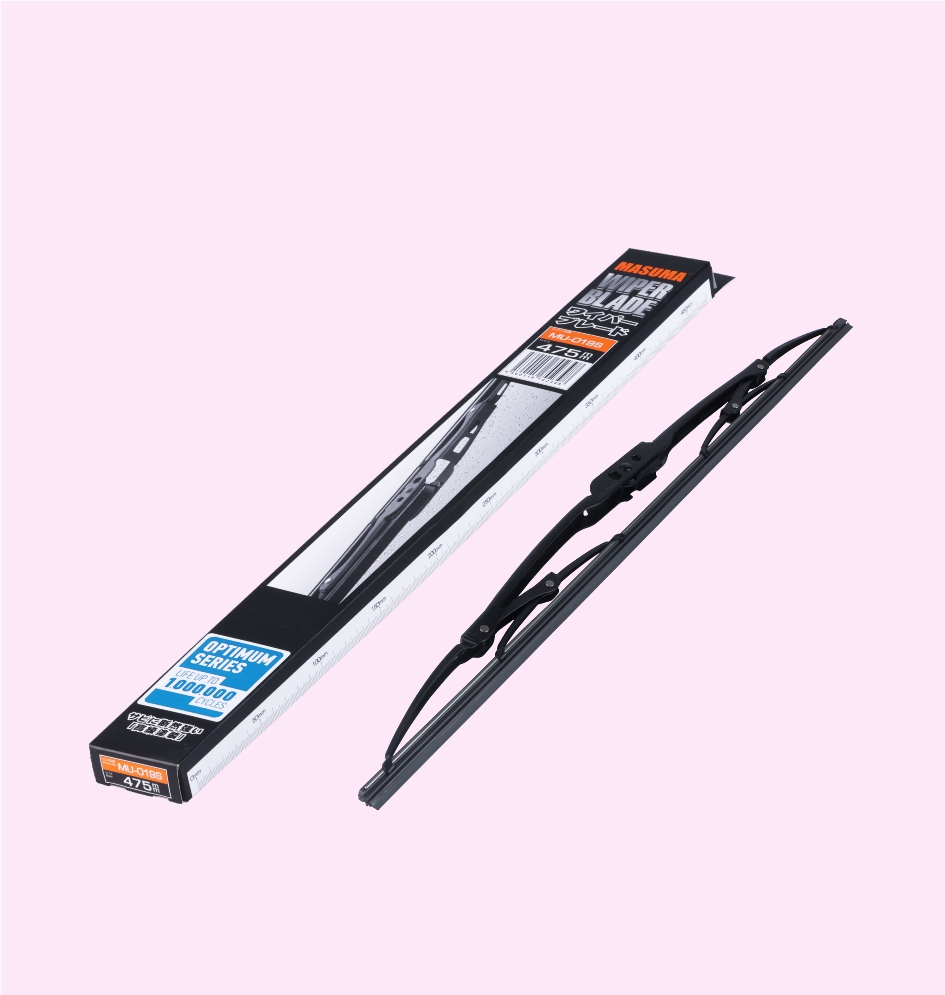
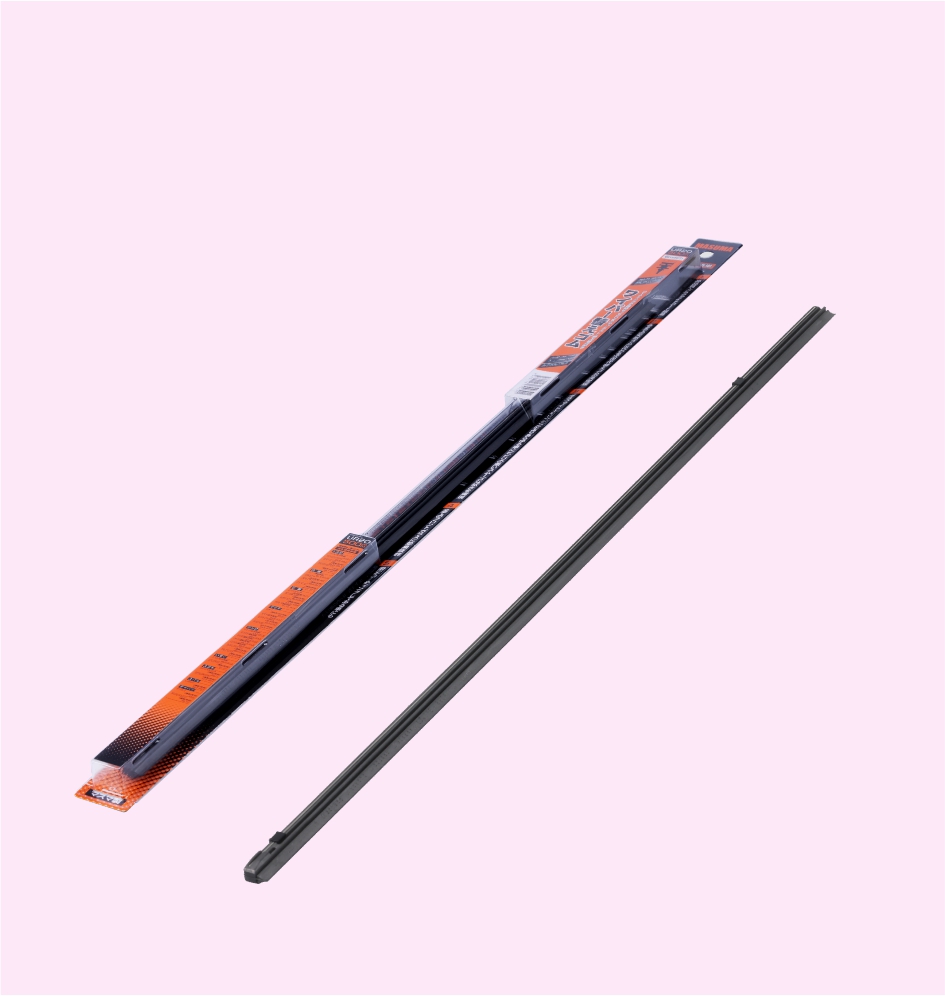
WIPER BLADE
BEAM WIPER BLADE
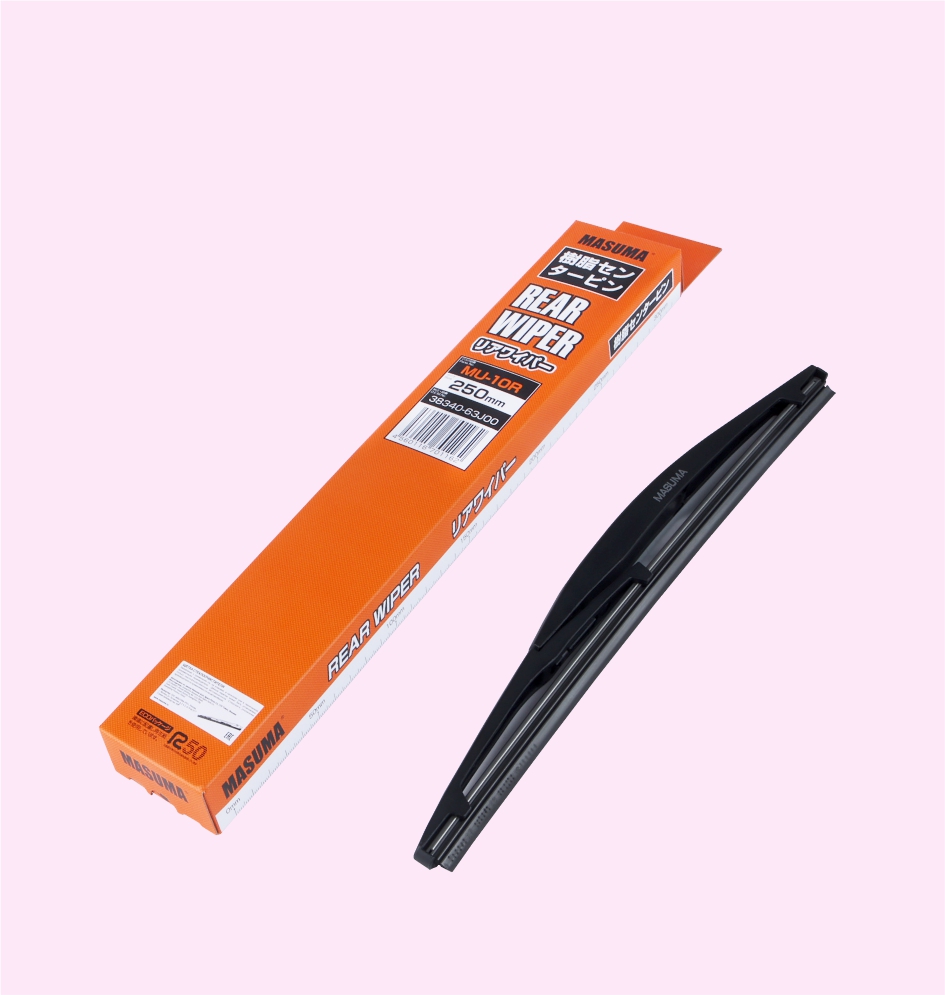
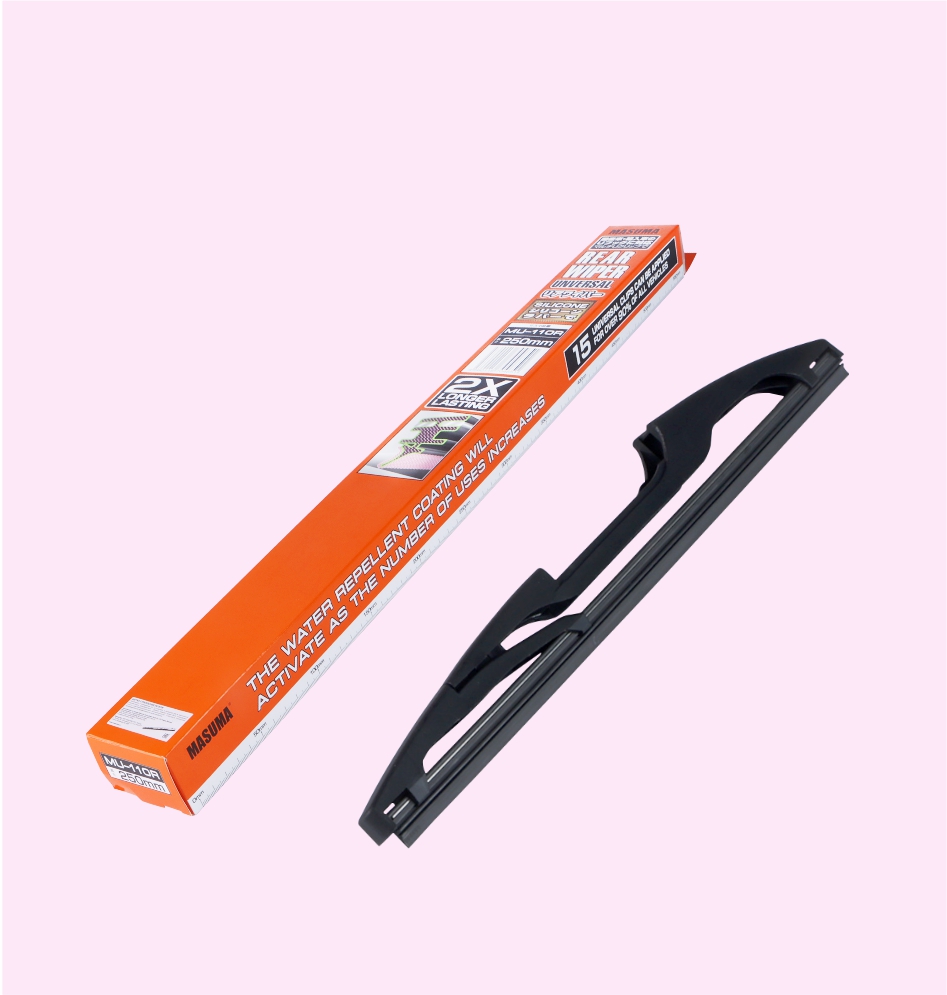
REAR WIPER
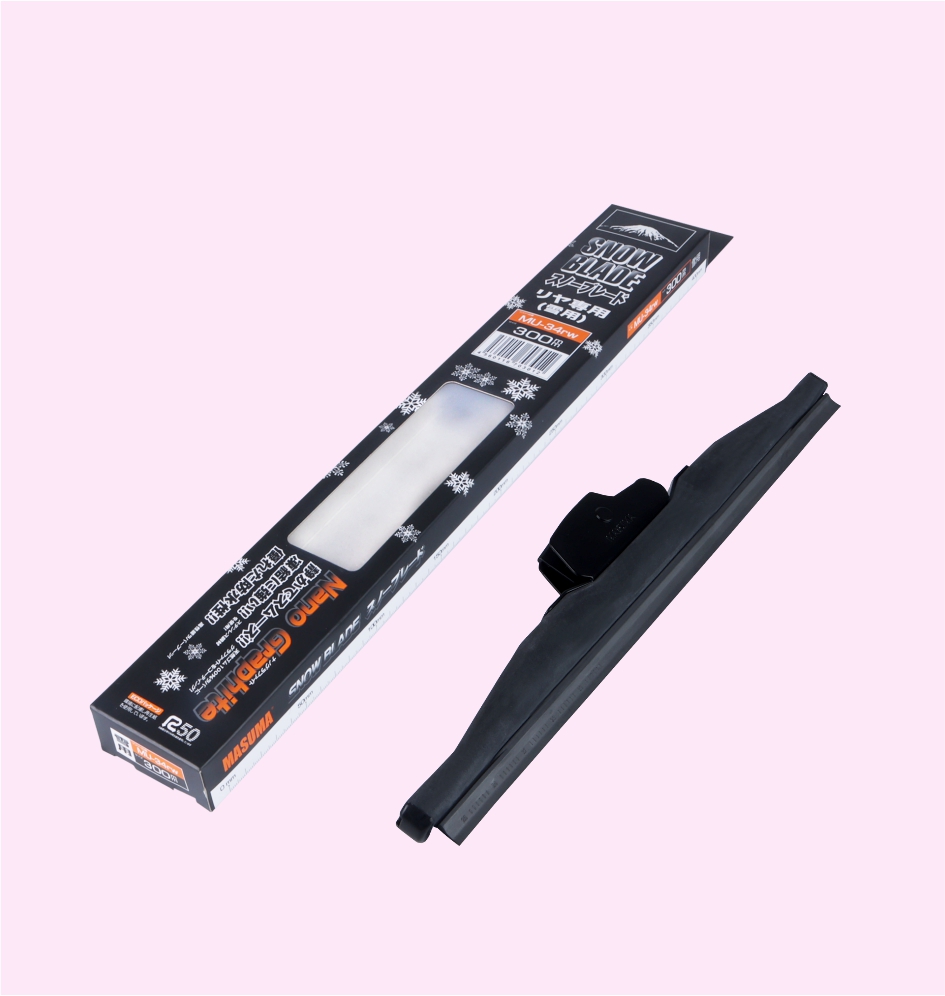
REAR SNOW BLADE
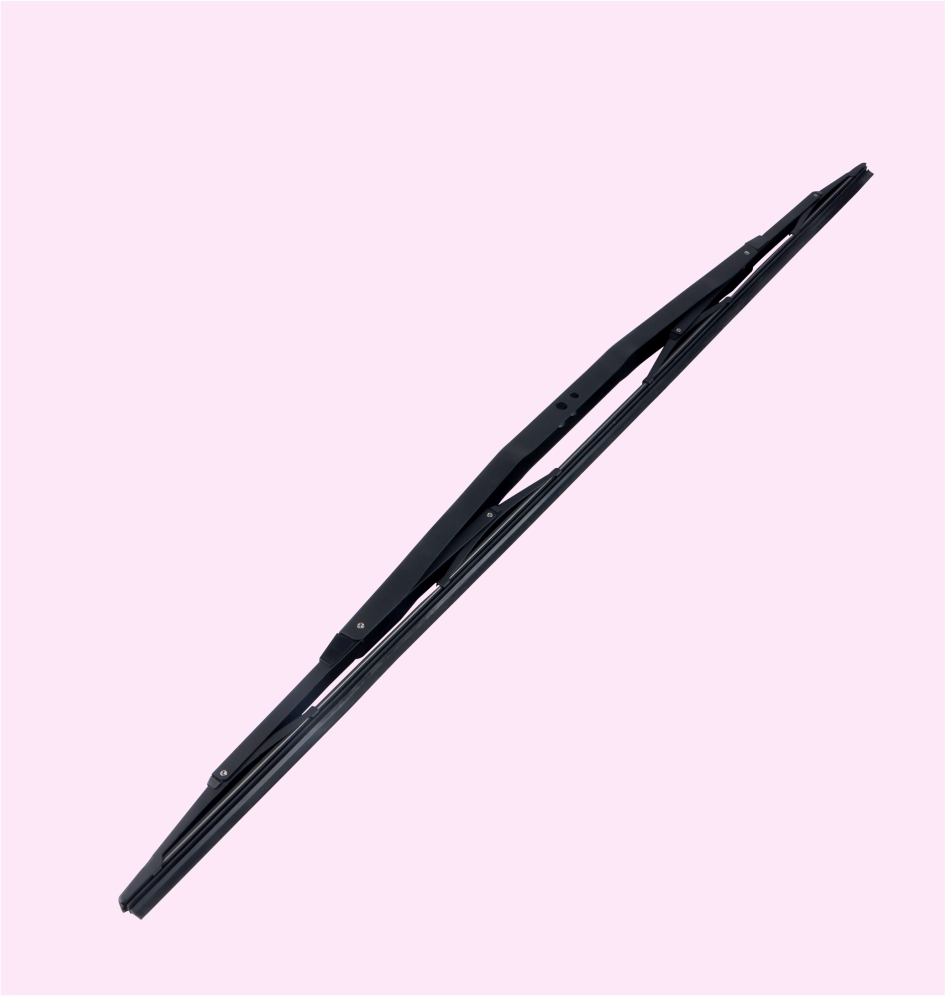
TRUCK WIPER
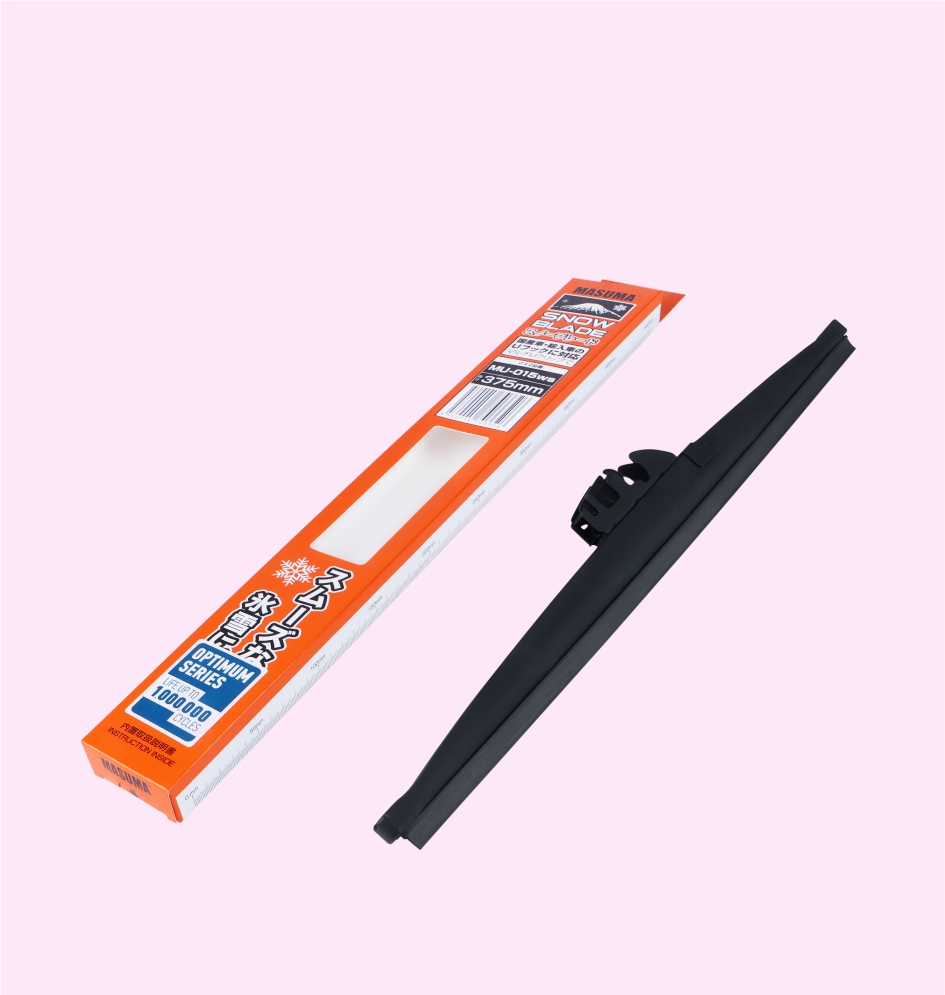
SNOW BLADE
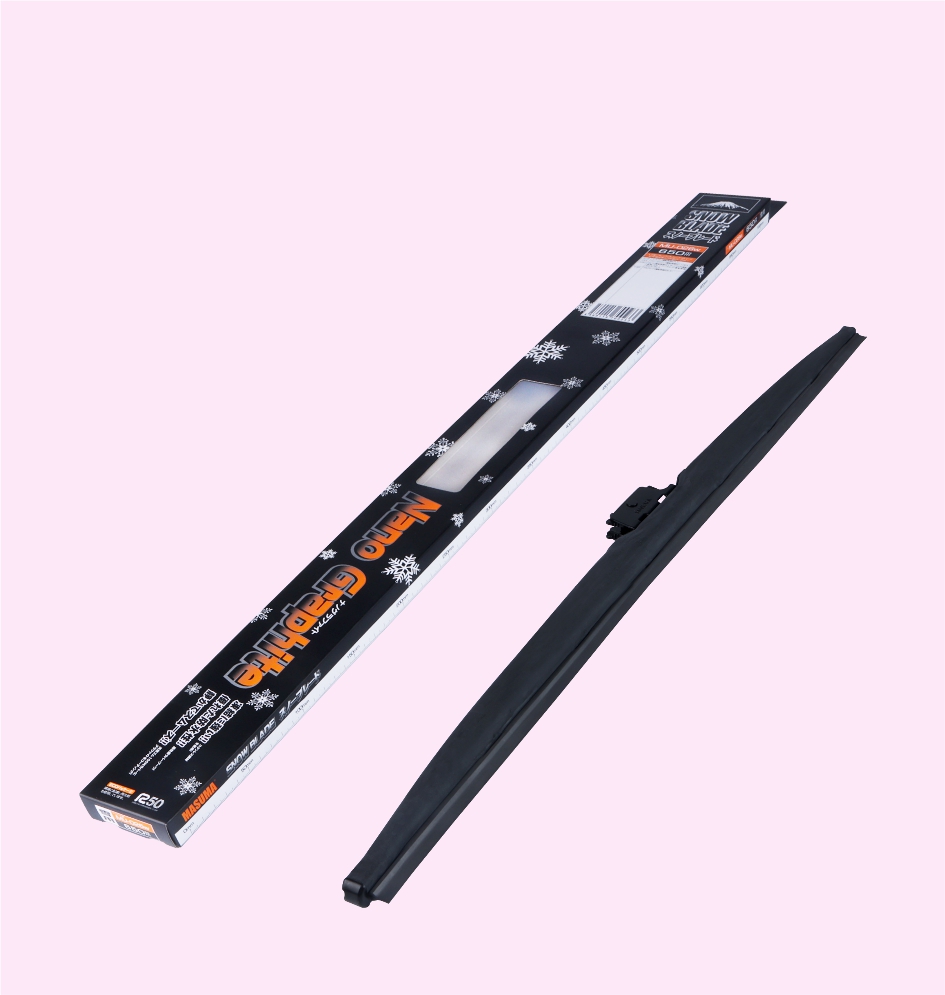
SNOW BLADE (NANO GRAPHITE)
FLAT WIPER BLADE
REAR WIPER (SILICONE UNVERSAL)
ALTERNATOR BEARING
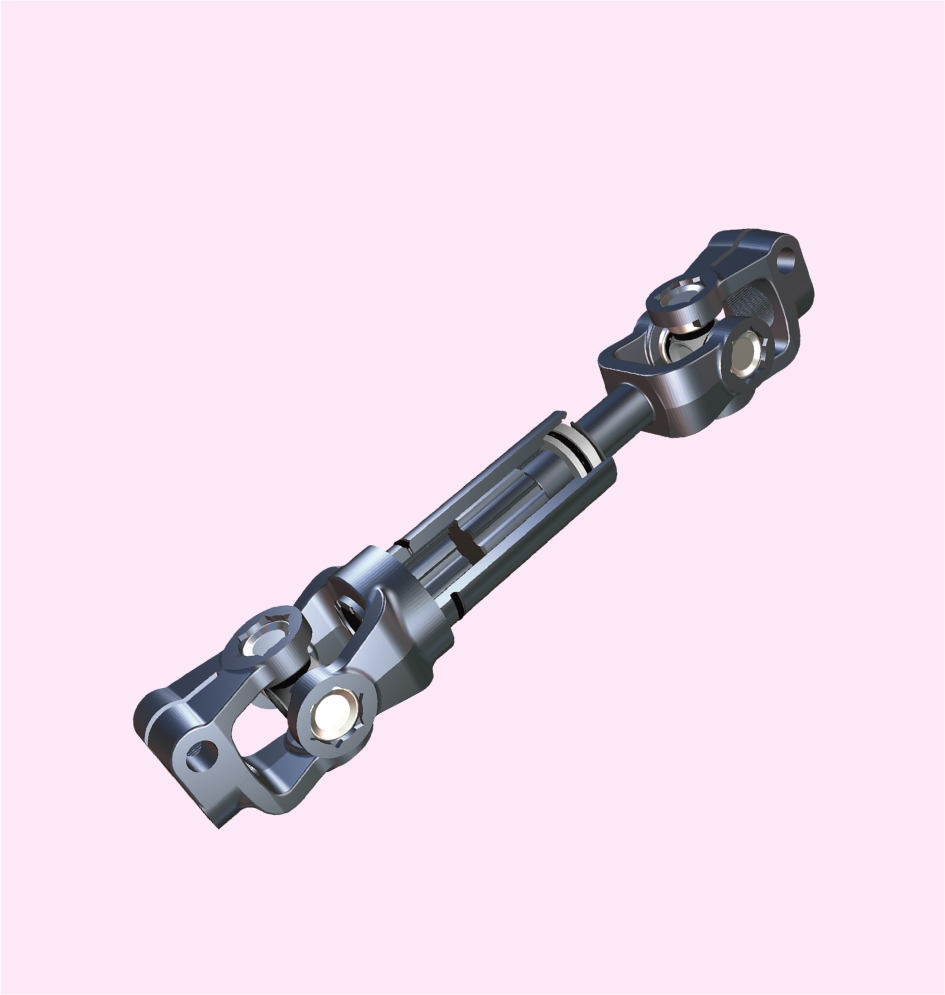
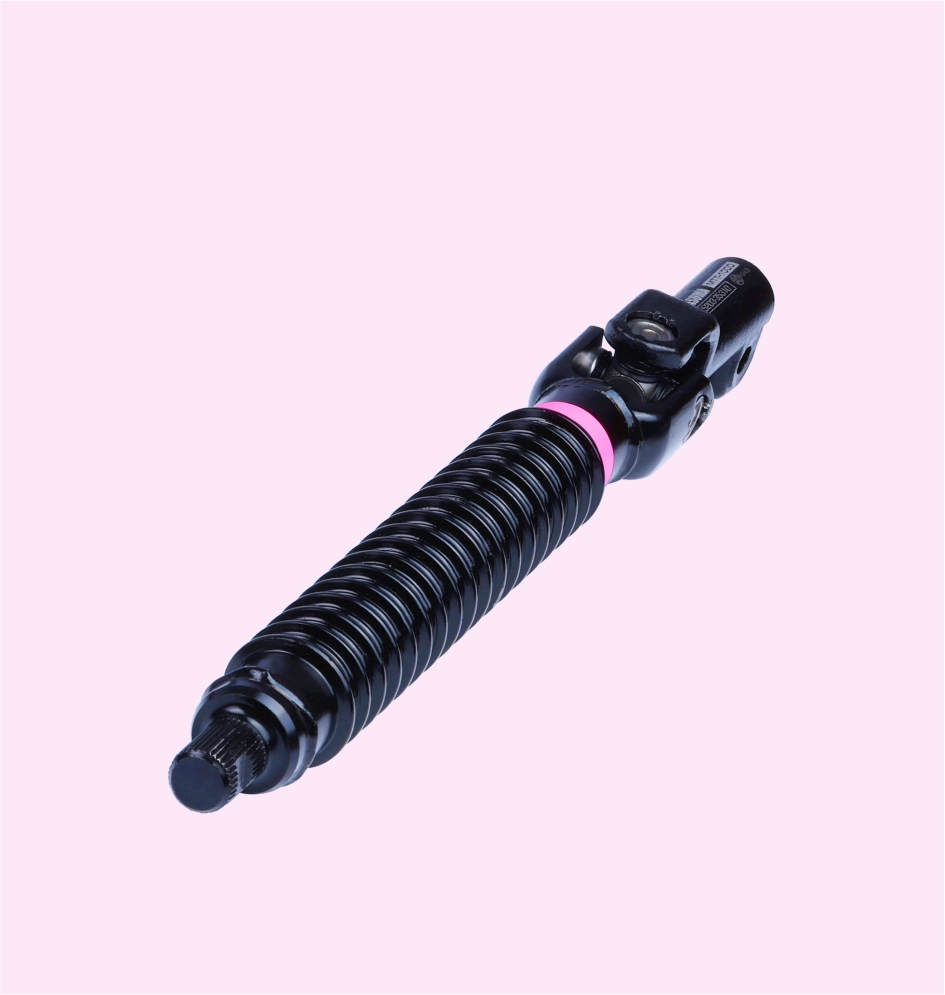
Steering Shaft
AIR SPRINGS
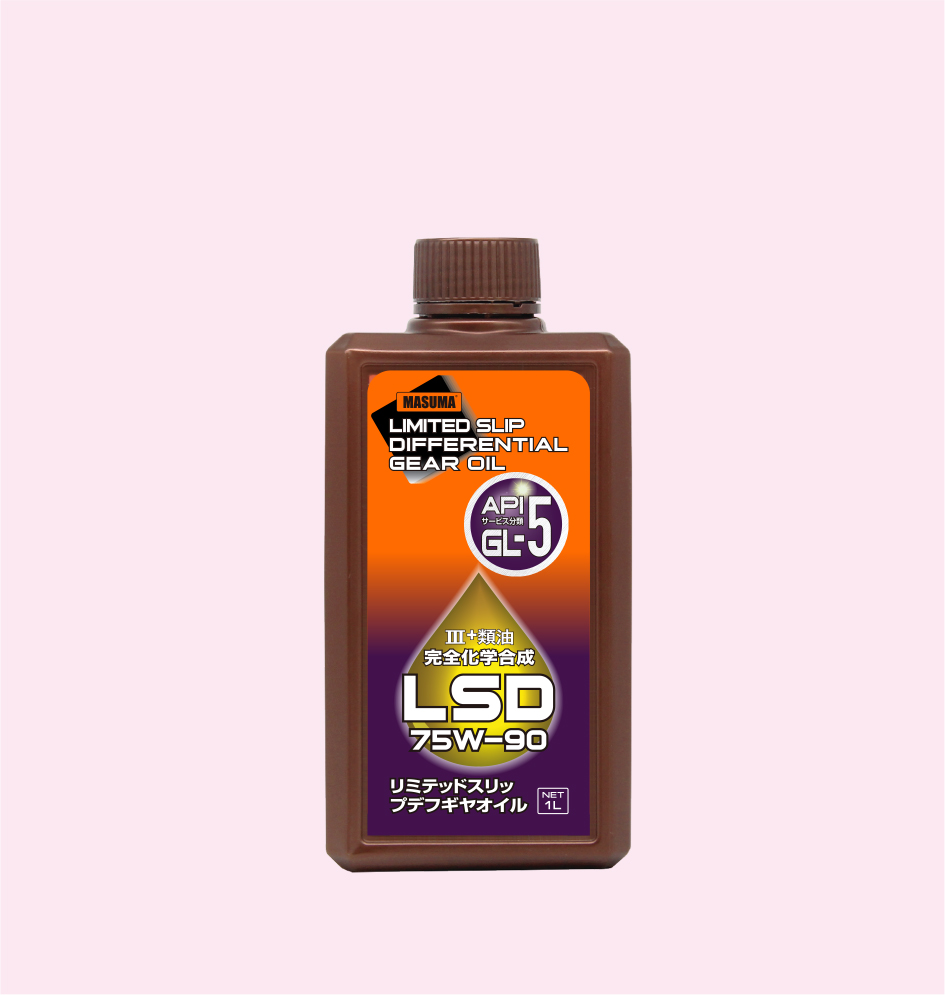
LIMITED SLIP DIFFERENTIAL GEAR OIL
TYRE REPAIR NAIL
INNER C.V. JOINT
VACUUM THERMOS FLASK(BLACK)
VACUUM THERMOS FLASK(PINK)
ENGINE PISTON
PISTON RING SET
CYLINDER LINER
ENGINE VALVES
FUEL LINE HOSE
CLUTCH OPERATING CYLINDER
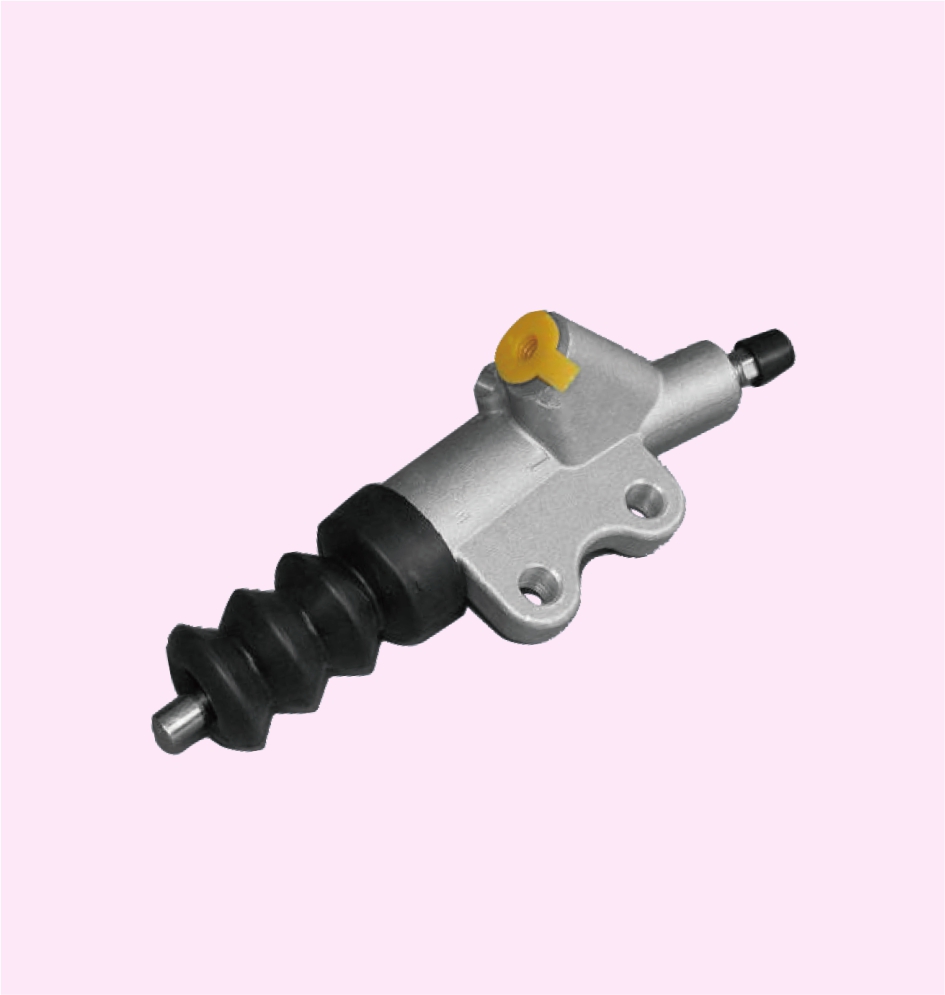
CLUTCH MASTER CYLINDER
CLUTCH CYLINDER REPAIR KIT
SIDE ROD ASSY
PITMAN ARM
IDLER ARM
AIR SUSPENSION COMPRESSOR
PARKING SHOE
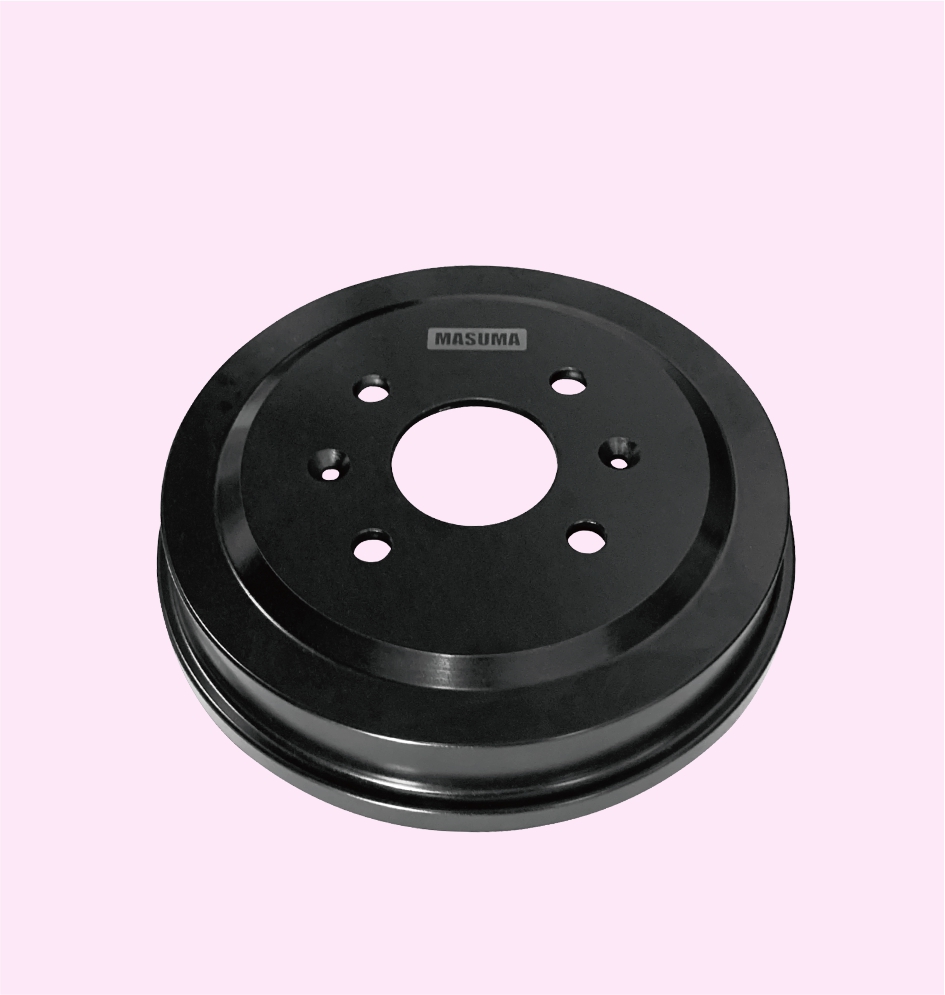
BRAKE DRUM
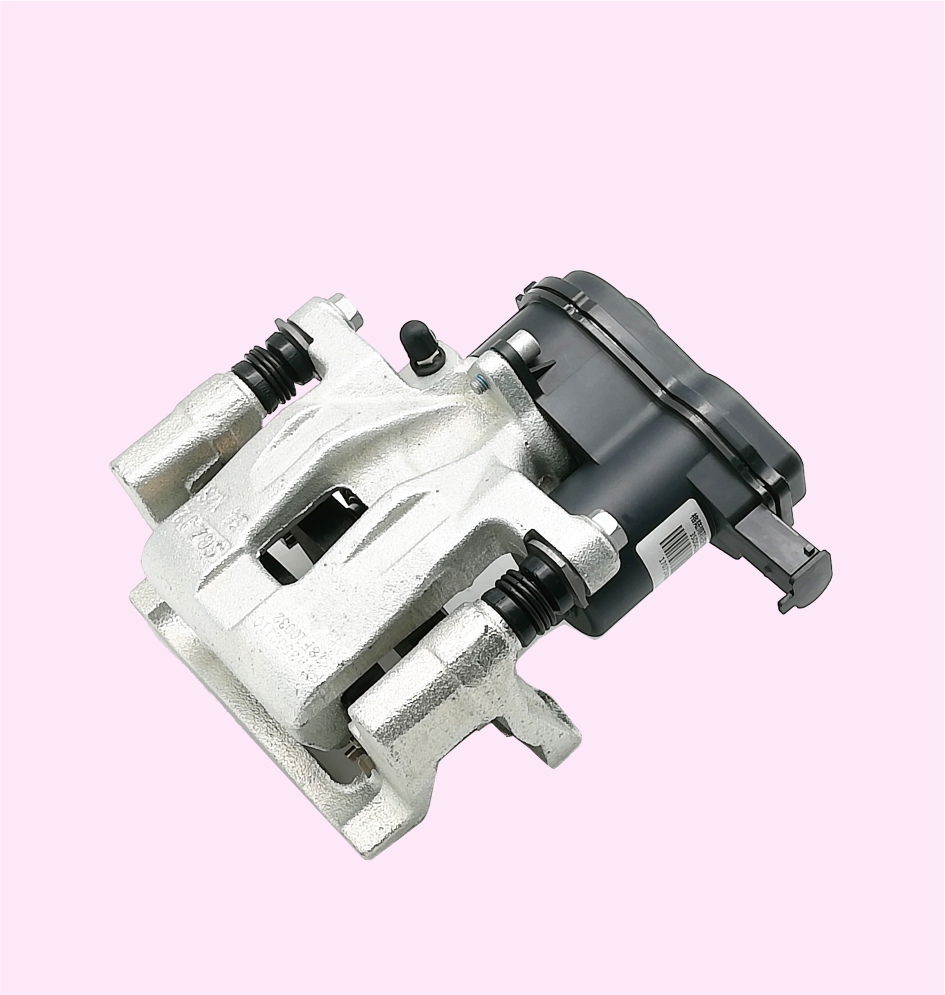
BRAKE CALIPER
DRIVE SHAFT BOOT KIT (TPEE)
DRIVE SHAFT BOOT KIT (SILICONE RUBBER)
STEERING BOOT (TPEE)
STEERING BOOT (SILICONE RUBBER)
FLAT JOINTS PIPE
Truck Wheel Hub Nut
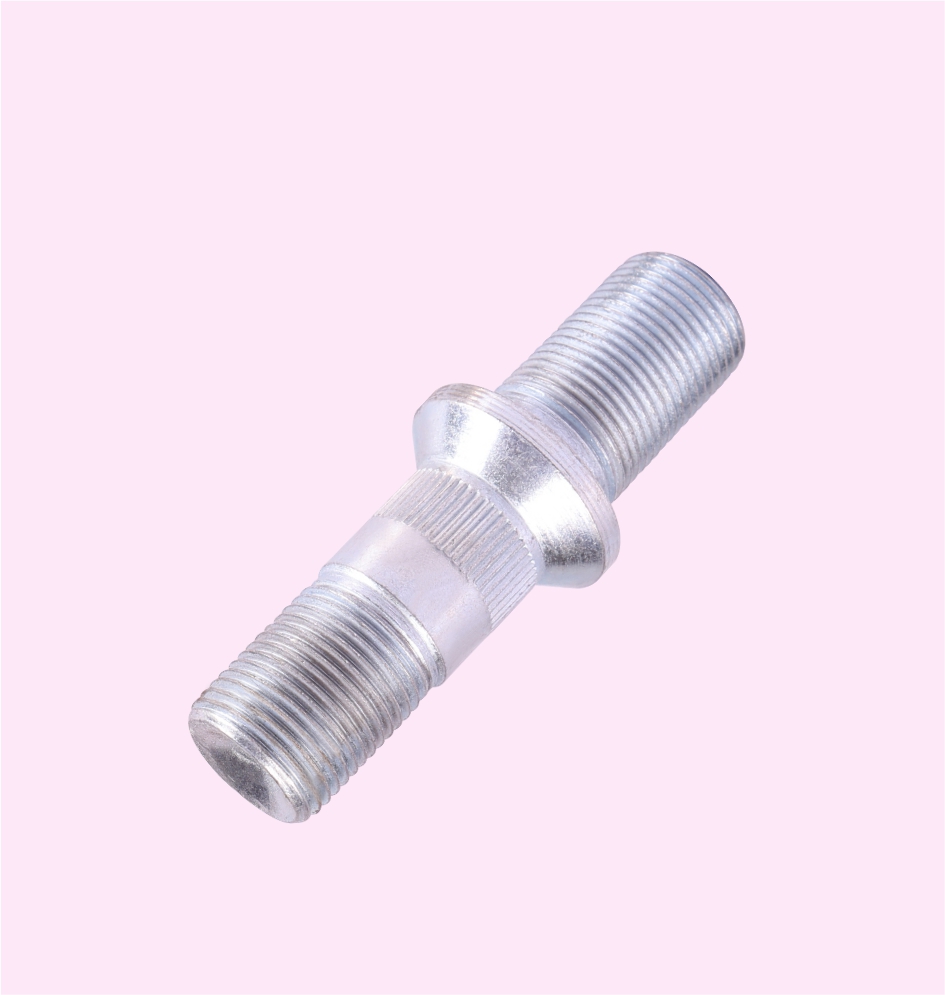
Truck Wheel Hub Bolt
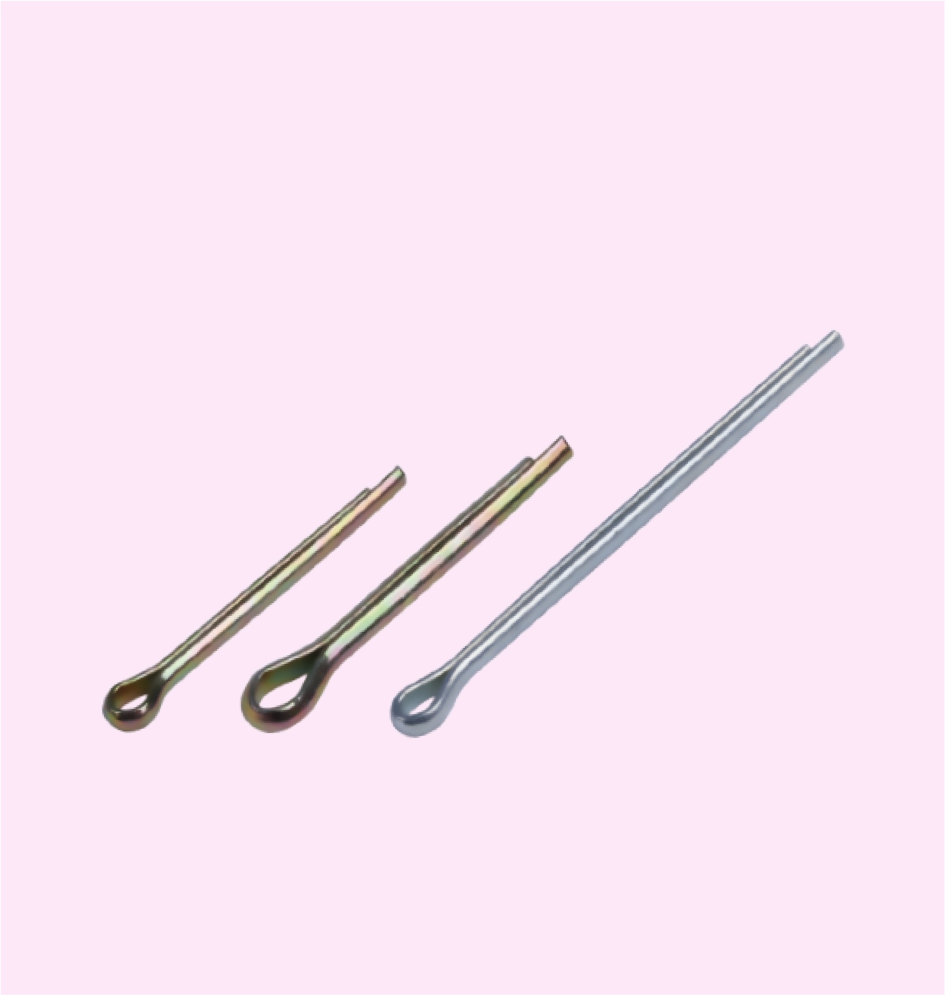
COTTER PINS
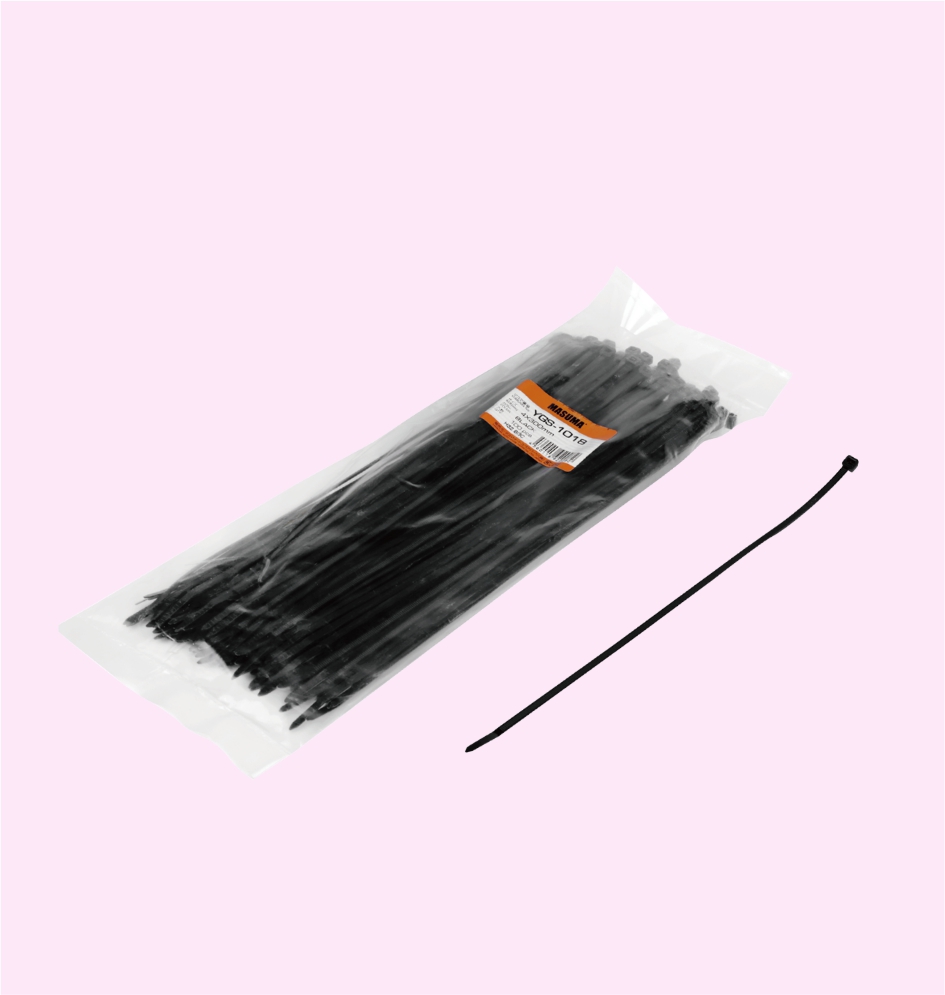
NYLON CABLE TIES
MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR CLEANER
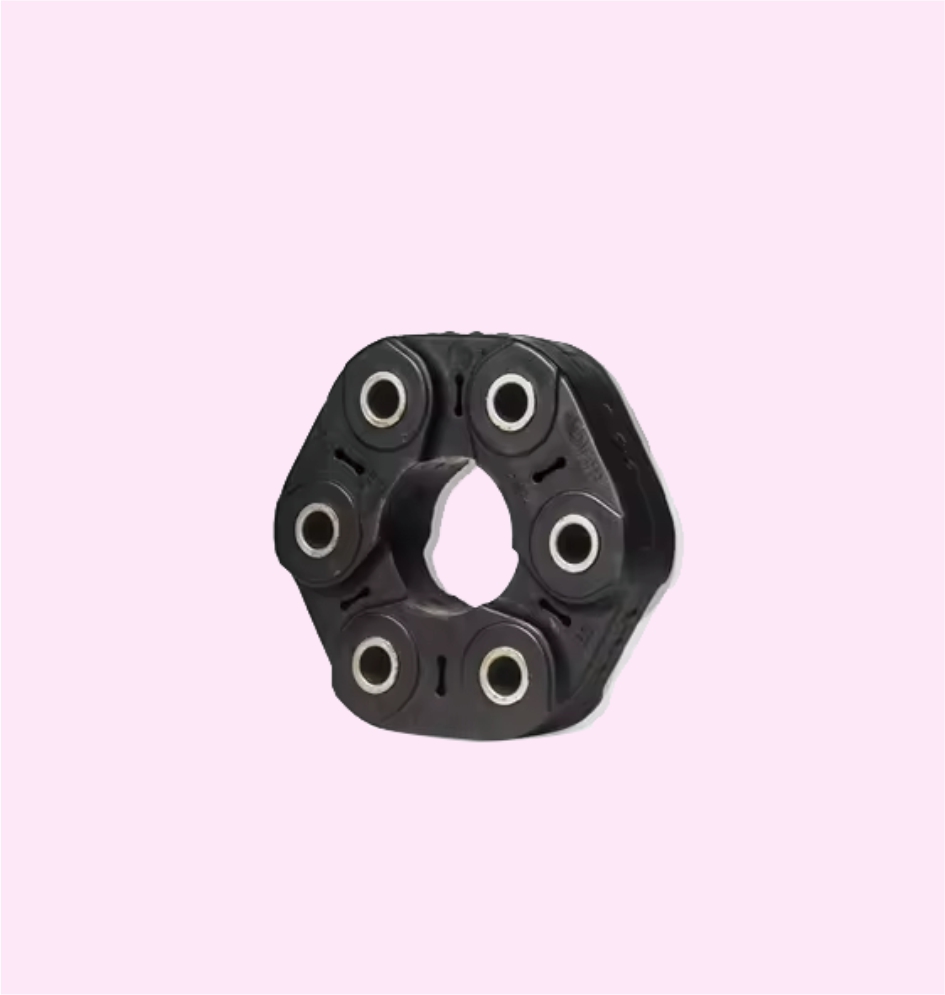
DRIVESHAFT COUPLING
HYBRID WIPER BLADE
AUTO BULBS
TIRE SHINE
FLAT WIPER BLADE
SHOCK ABSORBER DUST COVER
GASKET EXHAUST PIPE
Felt bag
Memo book
DISPLAY STAND
Long pants autumn outfit
T-SHIRT
Summer Green T-shirt
Orange shirt
Orange Polo Half Sleeve
Summer short sleeves
White long sleeved shirt
White long sleeved shirt
T-SHIRT
Autumn long sleeved suit
Winter cotton clothing
White Short Sleeve
Black short sleeved shirt
Autumn long sleeves
Sealing tape
card case
Square lightbox
Rectangular lightbox
lighter
Tank oil machine
Car trunk rope hook
LOGO lamp
Dragging money tray
mug
Key Chain
wall calendar
Ceramic water cup
pen container
Japanese advertising pen
Purchase Order
towel
Black ashtray
New sealing tape
tape measure
flagpole
Oil brochure
Yellow sticker
Black sticker
Black sticker
Leaf board pad
glove
Brake disc disc drive
Stickers
poster
poster
poster
poster
poster
poster
poster
poster
poster
poster
poster
Leaflets
Brake disc sample
Ball head sample
Oil filter wrench kit
The brochure
product catalog
new book
tool
paper cup
Grey power bank
Black power bank
Material gifts
Picture Frame
tissue
poster
Power of Attorney
Refrigerant thermometer
Picture Frame
Leaflets
Stickers
glove
glove
glove
Advertising television
Half length sleeve
Half length sleeve
poster
poster
Orange triangle neutral pen
COMPANY FLAG
COMPANY FLAG
COMPANY FLAG
COMPANY FLAG
Air flow meter
Fuel pipe rack
Radium colored plastic bag
Steering joint connector
lead screw
nut
Tire pressure sensor
Engine Systems

Drivetrain Systems


Suspension & Steering


Brake Systems


Dust cover Series


Air Conditioning System


Filter Series


Exhaust Gas Systems

Fastening Series


Body parts


Electrical Parts


Automotive lighting


Tire Repair Supplies


Chemical Goods Series


Lubricants & Fluids Series

Service tools & Equipment


Others


GET A FREE CONSULTATION